Abstract
Taking young Asian women as research object, this paper is to develop a 2D-3D non-contact body measurement and calculation method for daily dressing state used to generate the CWH (chest, waist, and hip) circumferences suitable for garment practical applications. The general research approach is ‘analyzing related curves of human body, finding their fitting functions and length calculating formulas through mathematical analysis and measuring experiment with large number of samples – extracting effective feature points data in daily dressing state by dynamic and static experiments – calculating such dimensions as width and thickness after curve fitting – generating CWH circumferences via formulas and making comparison’. The numerical results validate the 2D-3D method presented in this paper as a useful and effective approach. Being different from other 3D non-contact measuring methods, the authors provide a new way to get the CWH measurements in the condition of daily natural dressing, which not only optimizes the non-contact anthropometrics theory, but also breaks the static measuring mode. Furthermore, the bringing forth of the concept of ‘daily dressing state’ and the laboratory experiments of this paper would be worthy for practical use.
1. Introduction
As an important branch of clothing ergonomics, anthropometry is the groundwork ensuring clothing design and manufacturing. In contrast to the traditional contact measuring mode, non-contact ones can offer accurate and full-scale measured data to meet the demands of modern garment digital trend well. 3D scanning and 2D-3D conversion are the main measuring and calculating methods used in the field of non-contact anthropometry, especially the former is well-developed over the past two decades.
For 3D scanning, using laser is popular. Some researchers did related works. For example, Watanabe et al. [1] adopted a laser displacement meter to measure waist circumference and developed the new system for the non-contact measurement of abdominal cross section. Shang et al. [2] used artificial and three-dimensional laser measurement method, through which the sample data were collected in the same situation, to study the national and professional standard size measurement system. In the design of data standards, using statistical methods to analyze the data, and a comprehensive evaluation from two aspects of stability of instrument and data correlation. The practical application was taken as an example to study the tolerance range of standard data. The research works of Wang and Jiang [3] were based on the measurement principle of structured light, a laser rotating body scanning of non-contact measurement system. They gave the requiring of Made to Measure apparel production mode according to individual types and made calibration about body measurement and production in a line. Besides using laser, other researches about the method and application of 3D measuring also carried forward the non-contact measuring technique. Such as Zhang et al. [4] developed non-contact measurement of revolving body straightness method. They inspected a 1200 mm long rotating body with a spatial straightness error of a diameter of 160 mm in the 3D machine vision metrology. Pan et. al. [5] used C# and SQL database to design and implement for non contact 3D human body measurement in the human body database management system. Wang et. al. [6] proposed a non-contact 3D body data acquisition method for garment fit evaluation the distribution characteristics of the remaining space between the 3D scanning and clothing. The researches [7-10] used 3D non-contact measurement method to analyze body shape. Remondino [11] explored the generation of 3D models from uncalibrated image sequences. The study process also included the extraction of correspondences on the body using a least squares matching algorithm and the reconstruction of the 3D body model in point cloud form.
Some researches focused on 2D and 2D-3D non-contact measurement, such as Pirre and Shi [12] developed 2D image measurement system, which could determine the size of clothing. They found image-based systems were capable of providing anthropometric measurements, both in terms of accuracy and repeatability, which were better than traditional measurement methods. Yu et al. [13] adopted a wide coverage of optical design. This system could obtain high resolution images in a short distance, and through the computer program into a 3D human body model. Gu et al. [14] developed automatic pattern generation system of men’s pants, which is based on two dimensional non-contact human body measurement systems. Guo et al. [15] explored the application of the automatic clipping method in the 2Dimensional non-contact measuring system.
As for the dynamic measurement and application researches, non contact technology of human daily life activity detection include: Kurita [16, 17] developed a method for measurement of human motion, which was the electrostatic induction current non-contact type for walking motion detection. Umeda [18] developed of non-contact detection technology, which has been used to measure human vital signs. Deepak et al. [19] and Yutaka et al. [20] utilized 3D non-contact measurement method to discuss knee motion of human body. Kurita [21] developed an effective non-contact technique for the measurement of human stepping. Nicola [22] took advantage of cameras to measure and track moving surfaces of human body parts from multi-image video sequences acquired simultaneously. Yang et al. [23] adopted high speed camera to analyze the landing from different heights, the current research tries to figure out the landing vibration responses to different segments, including the lumbar, knee, hip, neck and the reacting force from ground.
Although the previous works improved the non-contact measuring technique gradually, two of the most common problems or challenges still exist: one is the limitation on the dress of subjects, the other is the static measuring mode. That is, relatively accurate measurements of human body parts can be obtained only when subjects still stand, wearing underwear or straitjacket. In view of garment size designation of the industry, this paper introduces a 2D-3D conversion approach to generate the CWH measurements in natural daily dressing state, no matter the measuring mode is dynamic or static. Experiments prove that this method, which is free from the dressing constrains and break the static mode, can meet the accuracy requirement. In our approach, through large sample measuring experiment showed in Section 2, laws of the relative curves, such as the silhouette curves of front, back, body side and the cross-section curves of chest, waist, hip of human body, were studied in Section 3, in which their suitable fitting functions and the integral formula of the typical CWH curves were ascertained. Next, in Section 4, on the premise of somatotype, in daily dressing state, static and dynamic experiments were carried to extract the effective feature points’ information. Then 2D measurements such as the width and the thickness were measured or calculated out. With the 2D-3D conversional formulas aforementioned, the CWH measurements would be calculated finally. These numerical results and analysis are presented and discussed in Section 5. Conclusion is given in Section 6. The research route is shown in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1Research route
2. Large sample anthropological measuring experiment
In order to ensure analysis credibility for the curves of silhouette and CWH cross-section, and the relative property between calculating measurements and actual measurements, it is necessary to build a large sample measurement database via traditional contact measuring experiment. In this paper, take Asian young women as research subjects, whose basic requirements are shown in Table 1. The sample size is 81 persons, who are random selected, determined by the known sample data of the earlier study, combining the confidence interval 95 % and the actual experimental condition. The accuracy of CWH measurements is 2 cm, according to the standard of garment size designation. Tape measure, ruler, height measure and curve plotter (Fig. 2) are the main measuring tools. Stature, Chest, Waist, Hip, heights of CWH, widths and depths of CWH, BP to BP, HP to HP, distances of C-W and W-H, Shoulder are the measuring parts, whose measuring methods refer to GB16160-2008-T. In addition, the cross section curves of CWH and the silhouette curves of front, back, and side of the 81 subjects are plotted by the curve plotter one by one. As the comparison of the later calculating measurements, measuring all the circumferences of CWH curves manually, the specific results are shown in Table 3.
Table 1Basic information of subjects
Age (years) | 18-26 |
Height (cm) | 145-175 |
Weight (kg) | 40-70 |
3. Relative curves analysis
Curves associated with the CWH measuring and calculating include the CWH cross-section curves and the silhouette curves of the front, back and side. It is not advisable to take any one sample’s curves as the analysis basis. Therefore, the typical representative curve figures are selected. Take the chest cross-section curve as example. Firstly, divide 81 samples into three types: 0.69-0.77, 0.78-0.83 and 0.84-0.95, according to the different radius ratios of chest width/depth. Secondly, make smoothing and symmetrical process to the original figures of curves in the same radius ratio range, then overlay them and determine the mean points. Lastly, choose the curve of moderate ratio as the representative chest cross-section curve.
Fig. 2Curve plotter

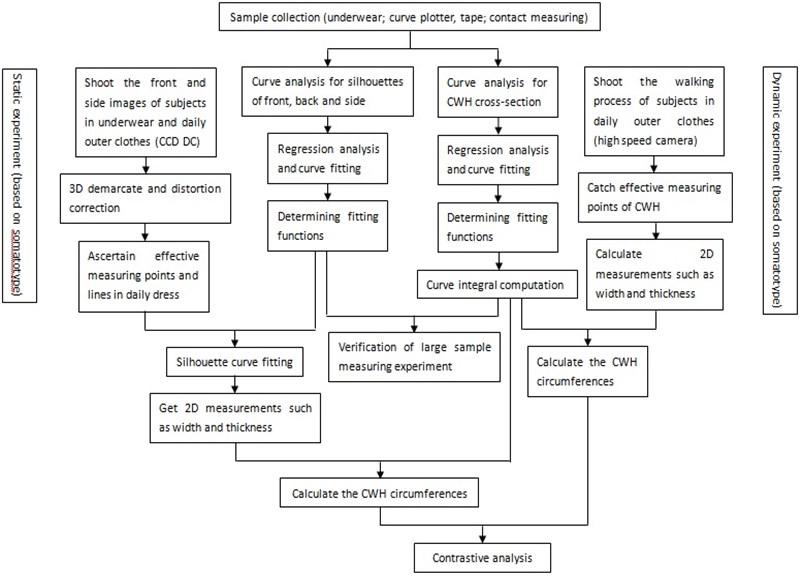
3.1. CWH cross-section curves
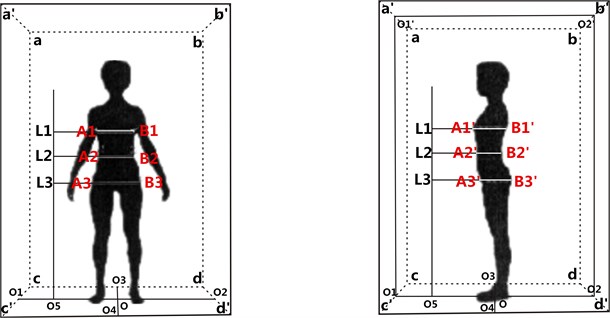
The typical CWH cross-section curves are shown in Fig. 3. For the convenience of analysis and formulation, plane-coordinate system is set up. For instance, the chest cross-section curve, as shown in Fig. 4, curve above -axis is the front chest curve, below is the back chest curve, segment is the chest width, is the chest thickness, is the front chest thickness, is the back one. 1/2 chest width, due to the symmetry of human body. Observe the trend of each segment curve, take the segment in (, 0) as example, a and b are the demarcation points, for arc , the tangent slope is larger, the curvature is less; for arc ab, the tangent slope is decreasing, the curvature is increasing; for arc , the tangent slope is minimum, the curvature is less.
Fig. 3The typical CWH cross-section curves
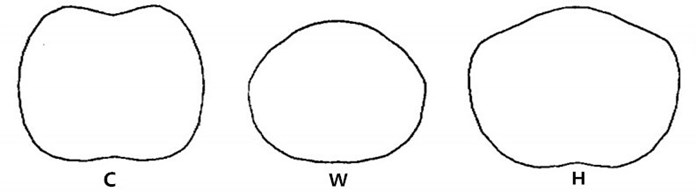
Fig. 4The typical CWH cross-section curves with XOY
3.1.1. Regression analysis
Before curve fitting and integrating, getting the thickness proportion of the front and back CWH curves is the premise. After measuring all the CWH curves obtained in the large sample experiment one by one, the regression formulas is acquired as Eq. (1). It should be noted that there are no difference of the width and thickness measurements after segmenting the CWH curves between using Eq. (1) and human judgment. Therefore, although the fitting confidences of the scatter plots are 0.43, 0.64, 0.51 respectively, there are no obvious significance to the final calculating results through experimental verification:
where is front, is back, is thickness, is chest and is waist.
3.1.2. Curve fitting
The existing typical methods of 2D-3D conversion for circumference measurements include super-elliptic curve fitting, EE parametric spline curve fitting, binary linear regression, and quadratic regression. It is found that the first two methods need a mass of statistic data and measuring points, and errors of the last two are larger, which cannot reach the accuracy requirement of this research. According to the principles of fewer measuring points, faster calculating, and higher precision, the logarithmic, trinomial, power, binomial curves are taken as the alternative fitting curves in this paper. Take the front waist curve as example, on which extract feature points evenly, make scatter diagrams of the aforementioned curve fitting, in that order, are 0.9884, 0.9865, 0.9281, 0.9052. After comparing and analyzing the situation of the extracted points and fitting curves, the study found that, for the front and back segments of the CWH cross-section curve, the confidence of the logarithmic curve fitting is the best, whose shape has the similar trend with the original. Thus, the logarithmic curve is confirmed as the fitting function finally.
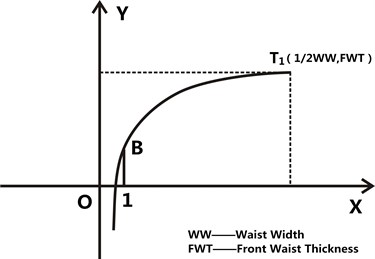
Take the 1/2 front waist curve (Fig. 5) as case study, its logarithmic curve equation is given as Eq. (2):
where is coefficient, is intercept.
Fig. 5The abridged general view of 1/2 front waist curve
3.1.3. Intercept B
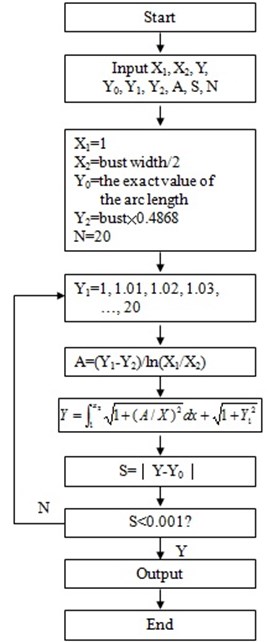
The discussion about the accurate intercept is given below. Undoubtedly, the logarithmic fitting curve determined by extracting the feature points precisely has the higher fitting precision. Measure the circumferences of 81 samples, calculate the integral computation of their circumferences through changing the intercept B using the successive approximation approach. Make them equal to the known measured circumference, and confirm the intercept , which is regarded as the precise one. The calculation procedure is presented in Fig. 6.
Fig. 6The calculation procedure of intercept B
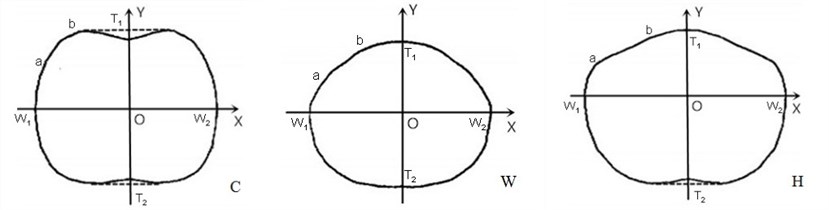
As for the intercept obtained using regression analysis, the relative work is described as follows. Through experiment and analysis, infer some kind of corresponding relation among the widths, thickness and the intercept . According to the expression of correlation coefficient (Eq. (3)), the correlation coefficients of the intercept and the widths, thickness are worked out.
In accordance with the correlation, the intercepts are fitted by multivariable linear regression. To make the data more accurate, the correlation test among the distance of -, the distance of - and the height, and the integral computation using different regression formulas are also conducted. After comparing errors of the integral results, Eq. (4) is written into integral program as this experimental result.
As for the intercept obtained using regression analysis, the relative work is described as follows. Through experiment and analysis, infer some kind of corresponding relation among the widths, thickness and the intercept . according to the expression of correlation coefficient (Eq. (3)), the correlation coefficients of the intercept and the widths, thickness are worked out.
In accordance with the correlation, the intercepts are fitted by multivariable linear regression. To make the data more accurate, the correlation test among the distance of -, the distance of - and the height, and the integral computation using different regression formulas are also conducted. After comparing errors of the integral results, Eq. (4) is written into integral program as this experimental result:
where is co-variation of and , , are variances of and .
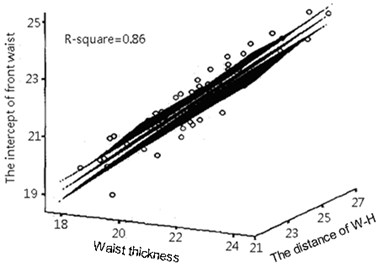
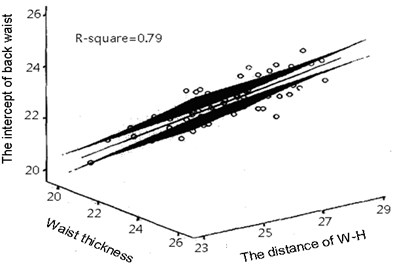
Fig. 7The scatter diagrams and responsive plane of the intercepts of the front and back waist
a)
b)
In Fig. 7:
where is hip.
Take the intercepts of the front and back waist as instance, Fig. 7 shows its scatter diagrams and responsive plane.
3.1.4. Circumference calculation of the fitted curves
On the basis of Eq. (2), the girth of the fitted curve is expressed as Eq. (5). The effective integral range is (1, 1/2 width), let 1/2 width, that is Eq. (6). The curvature of the curve in the range of (0, 1) is very small, and it cannot be extracted enough information and fitted in MATLAB, as a result, this paper employs the calculation method of hypotenuse (Eq. (7)) to obtain its approximate length. Through a large number of experimental verification, the error of this algorithm is minor:
3.2. Silhouette curves
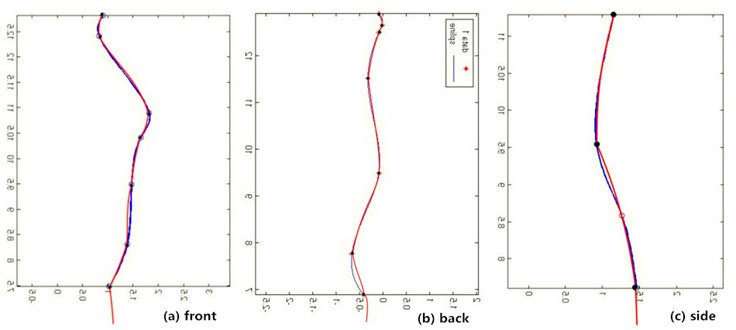
The analysis process and methods of this section is similar to the CWH cross-section curves presented in section 3.1. Here not repeat them because of the limited space. By research, the fitting functions of the silhouette curves of the front, back and side respectively are cscvn(), Spline Interplant and cscvn(). Fig. 8 shows their fitting comparison, in which the red is the typical body silhouette curves, and the blue is the fitted curves.
Fig. 8Fitting comparison
4. Static and dynamic experiment in daily dressing state
The basic information of subjects in these two experiments is as follows:
– age: 18-26;
– somatotype: thin, intermediate, plump;
– dressing types: blouse + trousers (jeans) of spring and autumn, T-shirt + tailored skirt (A-line skirt) of summer; sweater + jeans (pants) of winter.
Table 2Somatotype criterion
Index | Somatotype | ||
Thin | Normal | Plump | |
TNF | < 32 | 32-40 | > 40 |
Among them, the somatotype base is the body linear density index TNF, whose calculation is shown as Eq. (8). Table 2 shows the classification criterion. The reason why choose TNF is that TNF reflect the figure type feature of the Asian young people more better than the other universal methods such as girth difference, Rorel index, Verveck index and Bust/Height. In the base of somatotype and research of the previous large sample experiment, only three typical figure subjects are selected for case study in this section. The detailed steps are described as below:
where is weight (kg); is height (cm).
4.1. Static experiment
Main equipment: three dimensional calibration frame, fixed tripod, OLYMPUS C2500L digital camera, image capture card and a computer.
Indoor environment: room temperature 26 °C; ordinary fluorescent light.
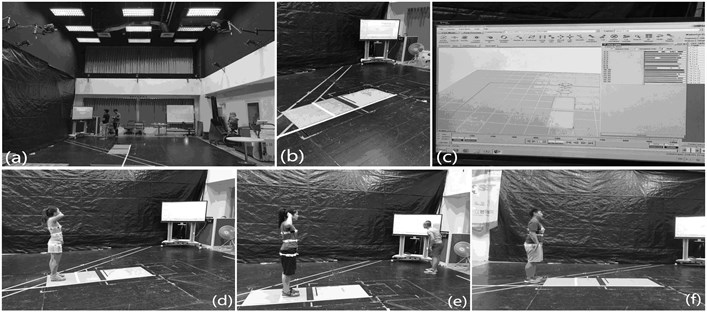
Experimental procedures: 1) Shoot the frontal and side digital images of each subject in sequence. In which, when shoot the front, the subject is required to do up hair, stand on the mark in the calibration frame, place feet shoulder width apart, raise arms whose angle with the body side is about 40°. Unlike the above, when shoot the side, the subject stand on the other mark, and her arms cling to the body without occluding the silhouette curves of the front and back. 2) Three dimensional calibration and distortion correction, to effectively reduce the measuring error caused by optical imaging. 3) Measure the related heights, lengths, and CWH widths and thicknesses. Fig. 9 shows the experimental diagrammatic sketch.
Fig. 9The static experiment arrangement
4.2. Dynamic experiment
Main hardware and software: 3D real-time motion analysis system, Raptor-E infrared high-speed camera, witch balls whose diameters are 1 cm, Cortex 3.0, and computer. Indoor environment is the same.
Fig. 10The dynamic experiment arrangement
Experimental procedures: 1) Bind elastic bands and paste witch balls on the BWH locations of the subjects in natural wearing state. 2) Test the range of capturing motion and debug the system. 3) Ask the subject walk as usual in the tested space. 4) The dynamic data of the witch balls are generated in the software system Cortex 3.0.
The experimental arrangement and scene are shown in Fig. 10(a) shows the site arrangement; (b) shows the walking area; (c) shows the system which reflects the dynamic situation of the featured points; (d), (e) and (f) show the subjects of three different figure types. Note: In dynamic experiment, influence of different dresses to the capturing process is less, owing to the binding band, thus only select the summer wearing model as the experimental wearing.
5. Numerical results and analysis
The results comparison between the calculating circumferences and measuring circumferences in the large sample experiment are shown in Table 3-Table 5.
Table 3Results of chest measurement of the large sample experiment
Sample No. | Calculating | Measuring | Error | Sample No. | Calculating | Measuring | Error |
75 | 80.83 | 82.30 | –1.47 | 70 | 76.90 | 76.90 | 0.00 |
39 | 80.44 | 81.90 | –1.46 | 19 | 78.61 | 78.60 | 0.01 |
55 | 79.65 | 81.10 | –1.45 | 60 | 86.11 | 86.10 | 0.01 |
76 | 75.66 | 77.10 | –1.44 | 10 | 79.28 | 79.20 | 0.08 |
66 | 78.84 | 80.20 | –1.36 | 23 | 81.73 | 81.60 | 0.13 |
61 | 83.24 | 84.60 | –1.36 | 25 | 79.93 | 79.80 | 0.13 |
30 | 80.75 | 82.10 | –1.35 | 81 | 82.64 | 82.50 | 0.14 |
27 | 81.78 | 83.10 | –1.32 | 72 | 79.76 | 79.60 | 0.16 |
56 | 87.43 | 88.70 | –1.27 | 74 | 87.36 | 87.10 | 0.26 |
37 | 82.06 | 83.30 | –1.24 | 53 | 77.37 | 77.10 | 0.27 |
52 | 82.26 | 83.40 | –1.14 | 15 | 78.51 | 78.20 | 0.31 |
43 | 77.24 | 78.20 | –0.96 | 16 | 83.22 | 82.90 | 0.32 |
18 | 74.15 | 75.10 | –0.95 | 41 | 78.68 | 78.30 | 0.38 |
45 | 72.85 | 73.80 | –0.95 | 69 | 73.30 | 72.90 | 0.40 |
80 | 80.40 | 81.30 | –0.90 | 54 | 74.21 | 73.80 | 0.41 |
35 | 82.76 | 83.60 | –0.84 | 9 | 80.92 | 80.50 | 0.42 |
50 | 84.89 | 85.70 | –0.81 | 77 | 83.03 | 82.60 | 0.43 |
12 | 78.17 | 78.90 | –0.73 | 5 | 84.43 | 84.00 | 0.43 |
34 | 89.14 | 89.85 | –0.71 | 29 | 82.55 | 82.10 | 0.45 |
57 | 82.57 | 83.20 | –0.63 | 20 | 76.10 | 75.60 | 0.50 |
48 | 79.08 | 79.70 | –0.62 | 51 | 86.04 | 85.50 | 0.54 |
44 | 82.66 | 83.20 | –0.54 | 47 | 80.69 | 80.10 | 0.59 |
13 | 76.69 | 77.20 | –0.51 | 8 | 78.66 | 77.90 | 0.76 |
24 | 78.93 | 79.40 | –0.47 | 63 | 82.79 | 82.00 | 0.79 |
73 | 77.85 | 78.30 | –0.45 | 68 | 79.60 | 78.80 | 0.80 |
7 | 78.96 | 79.40 | –0.44 | 28 | 82.51 | 81.60 | 0.91 |
67 | 77.76 | 78.20 | –0.44 | 17 | 79.62 | 78.70 | 0.92 |
6 | 78.21 | 78.60 | –0.39 | 49 | 83.56 | 82.60 | 0.96 |
14 | 83.41 | 83.70 | –0.29 | 3 | 79.78 | 78.80 | 0.98 |
58 | 83.99 | 84.20 | –0.21 | 59 | 81.01 | 80.00 | 1.01 |
11 | 77.72 | 77.90 | –0.18 | 32 | 83.72 | 82.70 | 1.02 |
65 | 78.63 | 78.80 | –0.17 | 33 | 84.07 | 83.00 | 1.07 |
78 | 80.75 | 80.90 | –0.15 | 31 | 81.77 | 80.70 | 1.07 |
79 | 85.20 | 85.35 | –0.15 | 62 | 74.67 | 73.60 | 1.07 |
46 | 76.97 | 77.10 | –0.13 | 40 | 83.08 | 82.00 | 1.08 |
71 | 74.69 | 74.80 | –0.11 | 22 | 78.61 | 77.40 | 1.21 |
42 | 78.80 | 78.90 | –0.10 | 26 | 81.74 | 80.50 | 1.24 |
36 | 84.44 | 84.50 | –0.06 | 4 | 78.75 | 77.50 | 1.25 |
64 | 80.78 | 80.80 | –0.02 | 2 | 80.50 | 79.20 | 1.30 |
1 | 78.19 | 78.20 | –0.01 | 38 | 77.64 | 76.20 | 1.44 |
21 | 77.50 | 77.50 | 0.00 |
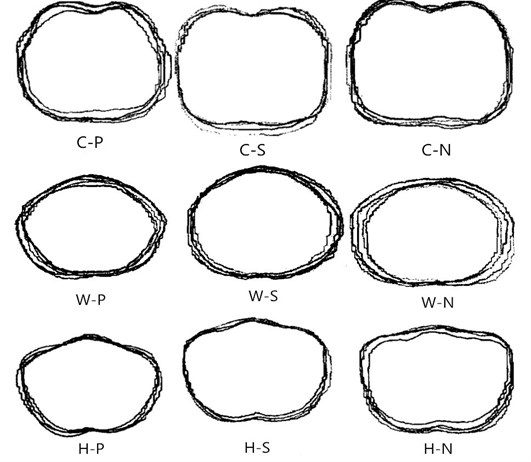
Table 3-5 show that, the absolute error of calculating CWH are respectively in (–1.47 cm~1.44 cm), (–1.50 cm~1.51 cm), (–1.60 cm~1.63 cm), which basically meet the requirement of ±1.5 cm in garment industry. The errors caused by the measuring and calculating process are improved as follows. Overlap and piece the 4-5 groups of curve figures of the largest positive and negative error and the minimal absolute error, as Fig. 11 shown. It can be seen that, curves of the lager positive error- P model, the negative error- N model and the smaller absolute error- S model have the similar traits in shape and trend. Classify CWH curves in the above cross-section shapes in advance, using image recognition. Calculate the intercept with different regression formulas for different types of curves, and then run the integrations. This process can decrease the error effectively.
Table 4Results of waist measurement of the large sample experiment
Sample no. | Calculating | Measuring | Error | Sample no. | Calculating | Measuring | Error |
58 | 72.10 | 73.6 | –1.50 | 1 | 67.50 | 67.7 | –0.20 |
74 | 70.18 | 71.6 | –1.42 | 33 | 68.34 | 68.5 | –0.16 |
14 | 66.41 | 67.8 | –1.39 | 22 | 62.85 | 63 | –0.15 |
44 | 62.22 | 63.5 | –1.28 | 80 | 69.66 | 69.8 | –0.14 |
75 | 66.00 | 67.2 | –1.20 | 36 | 69.81 | 69.9 | –0.09 |
68 | 63.23 | 64.4 | –1.17 | 34 | 74.91 | 75 | –0.09 |
67 | 59.54 | 60.7 | –1.16 | 7 | 62.24 | 62.3 | –0.06 |
17 | 60.50 | 61.6 | –1.10 | 53 | 64.05 | 64.1 | –0.05 |
28 | 66.89 | 67.8 | –0.91 | 52 | 68.77 | 68.8 | –0.03 |
18 | 58.36 | 59.2 | –0.84 | 57 | 63.60 | 63.6 | 0.00 |
72 | 62.87 | 63.7 | –0.83 | 48 | 62.12 | 62.1 | 0.02 |
45 | 59.58 | 60.4 | –0.82 | 70 | 57.92 | 57.9 | 0.02 |
41 | 58.70 | 59.5 | –0.80 | 21 | 60.05 | 60 | 0.05 |
78 | 66.90 | 67.7 | –0.80 | 51 | 72.09 | 72 | 0.09 |
65 | 62.04 | 62.8 | –0.76 | 13 | 61.60 | 61.5 | 0.10 |
26 | 60.59 | 61.3 | –0.71 | 30 | 62.95 | 62.8 | 0.15 |
54 | 56.19 | 56.9 | –0.71 | 40 | 65.50 | 65.3 | 0.20 |
71 | 60.30 | 61 | –0.70 | 39 | 65.01 | 64.8 | 0.21 |
31 | 67.06 | 67.7 | –0.64 | 19 | 64.91 | 64.7 | 0.21 |
62 | 58.98 | 59.5 | –0.62 | 63 | 66.81 | 66.6 | 0.21 |
9 | 66.59 | 67.2 | –0.61 | 61 | 69.39 | 69.1 | 0.29 |
25 | 66.24 | 66.8 | –0.56 | 49 | 68.30 | 68 | 0.30 |
5 | 69.07 | 69.6 | –0.53 | 32 | 74.27 | 73.9 | 0.37 |
64 | 62.37 | 62.9 | –0.53 | 66 | 59.82 | 59.45 | 0.37 |
35 | 66.98 | 67.5 | –0.52 | 81 | 67.25 | 66.8 | 0.45 |
23 | 65.88 | 66.4 | –0.52 | 38 | 62.58 | 62.1 | 0.48 |
20 | 61.28 | 61.8 | –0.52 | 46 | 60.89 | 60.4 | 0.49 |
69 | 59.09 | 59.6 | –0.51 | 79 | 69.30 | 68.8 | 0.50 |
75 | 69.30 | 69.8 | –0.50 | 24 | 61.21 | 60.7 | 0.51 |
37 | 68.75 | 69.2 | –0.45 | 8 | 62.12 | 61.55 | 0.57 |
2 | 61.45 | 61.9 | –0.45 | 59 | 62.10 | 61.5 | 0.60 |
60 | 70.16 | 70.6 | –0.44 | 55 | 67.31 | 66.7 | 0.61 |
27 | 64.49 | 64.9 | –0.41 | 11 | 59.63 | 59 | 0.63 |
56 | 70.80 | 71.2 | –0.40 | 47 | 70.12 | 69 | 1.12 |
29 | 66.61 | 67 | –0.39 | 10 | 60.23 | 59 | 1.23 |
15 | 64.76 | 65.1 | –0.34 | 3 | 64.94 | 63.7 | 1.24 |
16 | 68.26 | 68.6 | –0.34 | 6 | 62.06 | 60.8 | 1.26 |
73 | 61.48 | 61.8 | –0.32 | 4 | 63.11 | 61.8 | 1.31 |
42 | 66.33 | 66.6 | –0.27 | 50 | 69.03 | 67.6 | 1.43 |
77 | 68.27 | 68.5 | –0.23 | 12 | 67.71 | 66.2 | 1.51 |
43 | 65.88 | 66.1 | –0.22 |
The results and the comparisons between the calculating circumference s and the measuring circumference s of the static and dynamic experiments, in which all the subjects wear different daily clothes and their body shape were classified in advance, are shown in Table 6 and Table 7.
Table 6 shows that, different dressings have some impacts on the selection of the feature points and the circumference calculation of the fitted curves. When the subjects wear clothes of soft textured and elastic fabric, whose styles highlight the body curves and fit, the errors of the measuring experiment are less.
Table 5Results of hip measurement of the large sample experiment
Sample no. | Calculating | Measuring | Error | Sample no. | Calculating | Measuring | Error |
36 | 97.50 | 99.1 | –1.60 | 30 | 88.33 | 88.3 | 0.03 |
78 | 88.59 | 90.1 | –1.51 | 77 | 93.14 | 93.1 | 0.04 |
74 | 92.32 | 93.8 | –1.48 | 14 | 89.06 | 89 | 0.06 |
29 | 87.14 | 88.6 | –1.46 | 27 | 85.48 | 85.4 | 0.08 |
44 | 88.59 | 90 | –1.41 | 17 | 85.93 | 85.8 | 0.13 |
12 | 84.87 | 86.2 | –1.33 | 55 | 91.93 | 91.8 | 0.13 |
40 | 90.08 | 91.4 | –1.32 | 19 | 86.93 | 86.8 | 0.13 |
34 | 91.38 | 92.7 | –1.32 | 79 | 95.07 | 94.9 | 0.17 |
7 | 86.91 | 88.15 | –1.24 | 37 | 87.11 | 86.9 | 0.21 |
21 | 81.87 | 83.1 | –1.23 | 22 | 86.82 | 86.6 | 0.22 |
45 | 79.39 | 80.6 | –1.21 | 52 | 91.62 | 91.4 | 0.22 |
58 | 91.81 | 93 | –1.19 | 59 | 84.52 | 84.3 | 0.22 |
18 | 82.25 | 83.4 | –1.15 | 20 | 82.28 | 82 | 0.28 |
41 | 85.88 | 87 | –1.12 | 5 | 95.02 | 94.7 | 0.32 |
16 | 89.52 | 90.6 | –1.08 | 3 | 83.32 | 83 | 0.32 |
31 | 89.73 | 90.7 | –0.97 | 69 | 79.73 | 79.4 | 0.33 |
32 | 90.93 | 91.9 | –0.97 | 75 | 91.33 | 91 | 0.33 |
15 | 89.26 | 90.2 | –0.94 | 68 | 88.24 | 87.9 | 0.34 |
57 | 84.97 | 85.9 | –0.93 | 11 | 83.79 | 83.4 | 0.39 |
8 | 82.05 | 82.9 | –0.85 | 56 | 90.62 | 90.2 | 0.42 |
13 | 86.40 | 87.1 | –0.70 | 66 | 87.89 | 87.4 | 0.49 |
24 | 85.47 | 86.1 | –0.63 | 72 | 84.89 | 84.4 | 0.49 |
9 | 90.71 | 91.3 | –0.59 | 43 | 91.50 | 91 | 0.50 |
64 | 85.34 | 85.9 | –0.56 | 60 | 90.93 | 90.4 | 0.53 |
2 | 84.56 | 85.1 | –0.54 | 80 | 87.35 | 86.8 | 0.55 |
38 | 84.00 | 84.45 | –0.45 | 49 | 91.85 | 91.3 | 0.55 |
67 | 82.35 | 82.7 | –0.35 | 61 | 88.75 | 88.2 | 0.55 |
46 | 81.28 | 81.6 | –0.32 | 33 | 89.35 | 88.7 | 0.65 |
42 | 92.42 | 92.7 | –0.28 | 63 | 91.26 | 90.6 | 0.66 |
6 | 84.63 | 84.9 | –0.27 | 39 | 84.27 | 83.6 | 0.67 |
47 | 90.31 | 90.5 | –0.19 | 10 | 84.87 | 84.2 | 0.67 |
73 | 80.27 | 80.4 | –0.13 | 4 | 80.74 | 80 | 0.74 |
28 | 89.68 | 89.8 | –0.12 | 54 | 80.33 | 79.3 | 1.03 |
62 | 80.69 | 80.8 | –0.11 | 50 | 88.90 | 87.8 | 1.10 |
71 | 82.31 | 82.4 | –0.09 | 76 | 88.32 | 87.1 | 1.22 |
51 | 85.41 | 85.5 | –0.09 | 25 | 88.45 | 87.2 | 1.25 |
70 | 80.92 | 81 | –0.08 | 35 | 93.77 | 92.5 | 1.27 |
26 | 86.94 | 87 | –0.06 | 23 | 90.06 | 88.5 | 1.56 |
1 | 85.85 | 85.9 | –0.05 | 81 | 86.71 | 85.1 | 1.61 |
65 | 79.10 | 79.1 | 0.00 | 53 | 86.63 | 85 | 1.63 |
48 | 84.82 | 84.8 | 0.02 |
Table 7 shows that, although the information of the featured points captured from the subjects’ walking state is different, the calculated vales are less different, which can meet the industry requirement. Certainly, the function of binding bands is not ignored, but as the feasibility discussion of the method, this experiment provides a possibility. And it should be studied how to get rid of the binding bands and obtain the featured points’ data in the future practical application.
Table 6Results of the static experiment
Subject A (thin) | ||||
Dressing | Elastic underwear | Blouse +A-line skirt | T-shirt +A-line skirt | Sweater + jeans |
79.92 | 83.64 | 82.28 | 81.14 | |
61.92 | 64 | 63.78 | 62.44 | |
83 | 80.68 | 82.46 | 83.76 | |
Subject B (normal) | ||||
Dressing | Elastic underwear | Blouse + trousers | T-shirt + tailored skirt | Sweater + pants |
83.90 | 88 | 84.70 | 88.50 | |
66.14 | 70.52 | 68.50 | 70.84 | |
88.48 | 91.92 | 90.46 | 90.82 | |
Subject C (plump) | ||||
Dressing | Elastic underwear | Blouse + jeans | T-shirt +A-line skirt | Sweater + jeans |
93.02 | 95.26 | 93.08 | 91.58 | |
70.78 | 78.22 | 72.34 | 70.32 | |
99.14 | 100.24 | 100.1 | 101.2 | |
Table 7Results of the dynamic experiment
somatotype | Calculated values (cm) | Actual (cm) | Error range (cm) | ||||
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
Thin | 80.83 | 80.54 | 80.90 | 80.45 | – | 80.1 | 0.35~0.80 |
Normal | 85.22 | – | 84.74 | 84.35 | 84.75 | 84.9 | –0.55~0.22 |
Plump | 96.77 | 96.53 | 96.40 | 97.63 | 96.70 | 96.0 | 0.40~1.63 |
somatotype | Calculated values (cm) | Actual (cm) | Error range (cm) | ||||
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
Thin | 62.05 | 61.91 | 62.11 | 62.13 | – | 61.2 | 0.71~0.93 |
Normal | 70.42 | – | 69.79 | 70.25 | 70.49 | 69.0 | 0.79~1.49 |
Plump | 84.69 | 85.04 | 85.92 | 85.71 | 85.92 | 85.0 | –0.31~0.92 |
somatotype | Calculated values (cm) | Actual (cm) | Error range (cm) | ||||
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
Thin | 87.37 | 87.60 | 87.04 | 87.36 | – | 87.5 | –0.46~0.10 |
Normal | 99.79 | – | 100.18 | 100.29 | 99.94 | 100.5 | –0.71~–0.21 |
Plump | 104.01 | 104.66 | 104.39 | 104.86 | 105.02 | 105.4 | –1.39~–0.38 |
Fig. 11Actual CWH cross-section curves of different error type
6. Conclusions
Comparing the length dimension which can be obtained more easily, how to generate the girth using limited feature points is one of the main subjects in the field of 2D-3D non-contact anthropometry used for garment industry. Taking Asian young women as researching objects, by regression analysis and curve fitting, algorithms of the circumferences were presented in this paper. As for the daily dressing state and the dynamic measuring mode, representative experiments were conducted, which had guidance meaning for making non-contact body measurement more convenient. By extracting the feature points in natural wearing state, static and dynamic, and using the algorithms mentioned above, the measurements were well obtained. This process is effective and provides a foundation for the rapid shape recognition and classification.
References
-
Watanabe A., Seno S. I., Kobayashi H., Kato S., Shimazu H. Development of non-contact body cross-section measurement system and evaluation for the practical use. Transactions of Japanese Society for Medical and Biological Engineering, Vol. 49, Issue 1, 2011, p. 156-162.
-
Shang X. M., Chen J., Wang Z. Y. Stability and Correlation analysis of data obtained by contact and non-contact measuring body. Advanced Materials Research, Vol. 156, Issue 157, 2011, p. 600-606.
-
Wang Y., Jiang S. S. The laser rotating of non-contact body scanning system. Journal of Fiber Bioengineering and Informatics, Vol. 8, Issue 1, 2015, p. 91-103.
-
Zhang S. X., Liu Y. L., Liu W. L., Ran D. G., Wang J. C. Non-contact measurement of revolving body straightness. Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on Instrumentation Science and Technology, 2002, p. 132-136.
-
Pan L., Yao T., Yao C., Wang J. Stability and correlation analysis of data obtained by contact and non-contact measuring body. Advanced Materials Research, Vol. 1048, 2014, p. 545-549.
-
Wang Z., Zhong Y. Q., Chen K. J., Ruan J. Y., Zhu J. C. 3D human body data acquisition and fit evaluation of clothing. Advanced Materials Research, Vol. 989, Issue 994, 2014, p. 4161-4164.
-
Zhang X., Wang Y. Y., Ran L. H., Feng A. L., He K. T., Liu T. J., Niu J. W. Human dimensions of Chinese minors. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 6777, 2011, p. 37-45.
-
Yang M., Guo P. P., Gu B. F., Liu G. L. Analysis of body shape differences of young males in south and north China. Textile Bioengineering and Informatics Symposium Proceedings, 2014, p. 891-898.
-
Wu Z. Z., Liao S. S., Nie L., Wang Z., Wang C. H., Zhou S. H. Design and implementation of human size measurement system based on images. Journal of Hunan University Natural Sciences, Vol. 37, Issue 9, 2010, p. 88-92.
-
Gu B. F., Liu G. L. Automatic modelling of the lower bodies of young females based on digital photographs. Journal of Fiber Bioengineering and Informatics, Vol. 7, Issue 2, 2014, p. 247-260.
-
Remondino F. 3-D reconstruction of static human body shape from image sequence. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, Vol. 93, 2004, p. 65-85.
-
Pirre M., Shi Y. Performance of a 2D image-based anthropometric measurement and clothing sizing system. Applied Ergonomics, Vol. 31, 2000, p. 445-451.
-
Yu W., Ng R., Yan S. CubiCam – a new approach of 3D body scanning system. Journal of HongKong Polytechnic University, Vol. 28, 2002, p. 55-62.
-
Gu B. F., Kong H. Y., Gu P. Y., Su J. Q., Liu G. L. Study of 2D non-contact anthropometric system and application. Proceedings of International Conference on Future Computer Sciences and Application, 2011, p. 150-153.
-
Guo P. P., Liu G. L., Dai H. Q. The application of automatic clipping in 2D non-contact measuring system. Textile Bioengineering and Informatics Symposium Proceedings, 2015, p. 589-595.
-
Kurita K. Novel non-contact and non-attached technique for detecting sports motion. Measurement: Journal of the International Measurement Confederation, Vol. 44, Issue 8, 2011, p. 1361-1366.
-
Kurita K. Human physical activity measurement method based on electrostatic induction. 11th IMEKO TC14 Symposium on Laser Metrology for Precision Measurement and Inspection in Industry, 2014, p. 82-85.
-
Umeda T., Takagi R., Jyo K. Non-contact monitoring system for body pose and respiration with radar sensor. 52nd Annual Conference of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineers of Japan, 2013, p. 2372-2373.
-
Deepak S., Tavakoli M., Atkinson P., Anseth S., Raley T., Walter N. External knee geometry surface variation as a function of subject anthropometry and flexion angle for human and surrogate subjects. SAE Technical Papers, 2007.
-
Yutaka A., Akinori S., Hiroshi H., Sho Y., Yasuhiro O., Hideki M. A method for non-contact measurement of knee load in sport motion. IEEE, 2007, p. 2724-2729.
-
Kurita K. Development of non-contact measurement system of human stepping. SICE Annual Conference, 2008, p. 1067-1070.
-
Nicola D. A. Surface measurement and tracking of human body parts from multi-image video sequences. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Vol. 56, 2002, p. 360-375.
-
Yang C. H., Lin P. C., Chiu Y. J. The vibration response analysis of segments in human body landing. International Symposium on Sports Biomechanics, 2007, p. 199-200.
Cited by
About this article
All the research works are supported by Fujian Social Science Project (FJ2016C118), Fujian Nature Foundation (2016J01039), Xiamen University of Technology Talent Foundation (YKJ15027R), Xiamen City Project (3502Z20173037).
