What's new
Editor's pick
Research Article
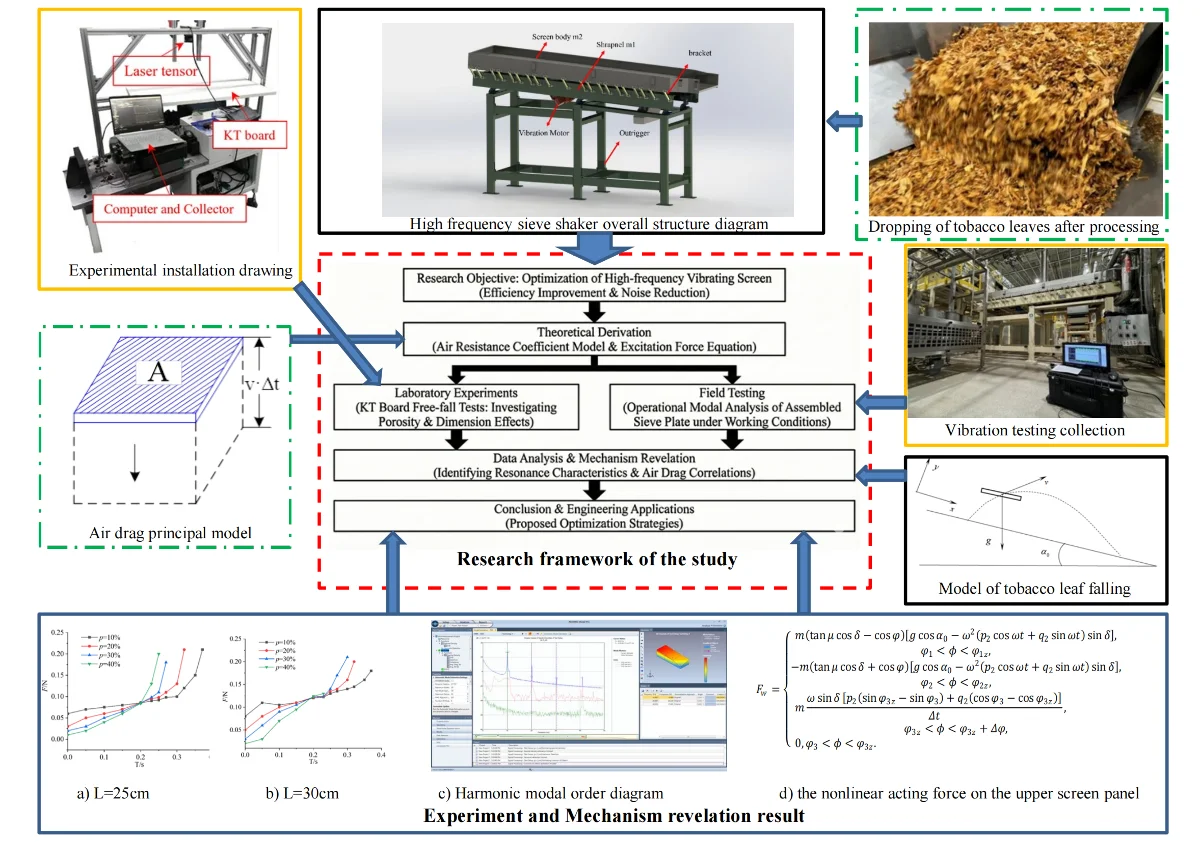
The airflow behavior of light particulate materials during free fall and their impact dynamics on screening surfaces
By Yang Wang, Jianyu Chang, Xiaoman Liu
To optimize the efficiency and noise performance of high-frequency vibrating screens, this study investigates the airflow behavior of lightweight materials during free fall and their impact dynamics on the screening surface. Based on the energy conservation theorem and the characteristics of tobacco screening, a computational model for the air resistance coefficient was derived. KT board specimens were employed as experimental substitutes for tobacco leaves to examine the effects of porosity and geometric dimensions on descent velocity and air resistance. The results indicated that materials with higher porosity exhibited greater descent velocities and lower air resistance, whereas larger geometric dimensions lead to increased aerodynamic drag and higher resistance coefficients. Furthermore, field operational modal analysis revealed that the sieve plate exhibited subharmonic resonances within the 9.9-10 Hz and 20-30 Hz frequency bands under nonlinear excitation. These findings could provide theoretical and data support for structural optimization aimed at noise reduction and screening efficiency enhancement.
February 11, 2026
Mechanical Engineering
Research Article
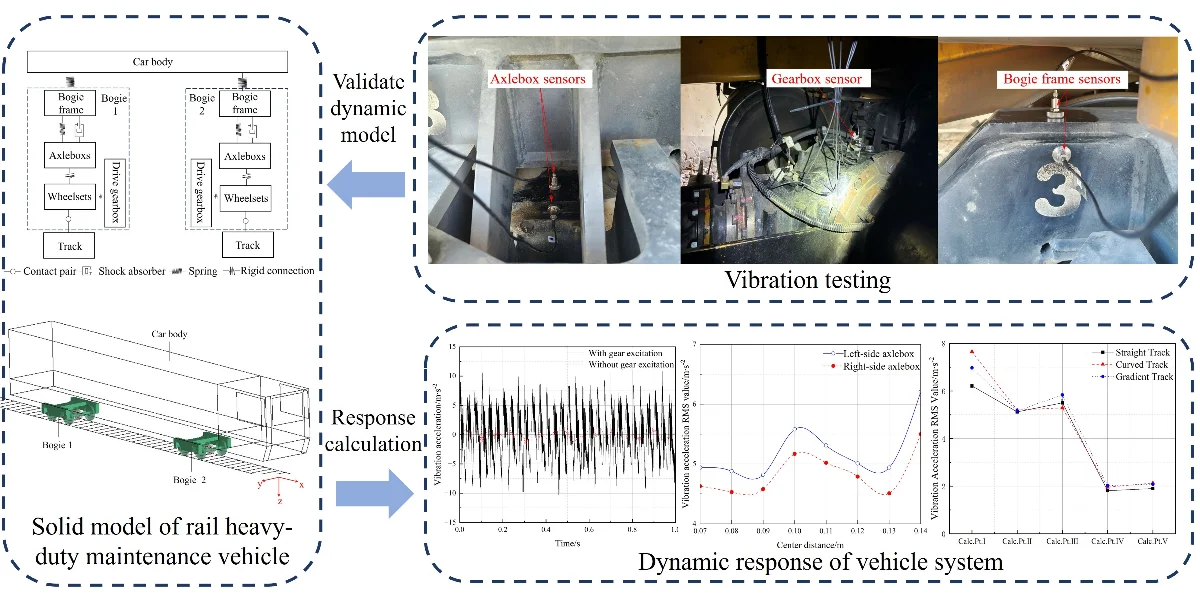
Dynamic characteristics and experimental study of rigid-flexible coupling for rail heavy-duty maintenance vehicle
Railway large-scale maintenance vehicles are key equipment for track maintenance. To investigate their dynamic operational characteristics, a dynamics model incorporating multi-rigid-flexible coupling components was developed, and its validity was verified through full-scale vibration tests. The results indicate that: gear system excitation has a significant influence on the vibration characteristics in the X-direction and Y-direction of the vehicle system, so in the dynamic simulation model of heavy-duty maintenance vehicles, gear system excitation load must be considered. As the center distance between the drive gearbox and axle decreases, the root-mean-square value value of vibration of the axleboxes on both sides are reduced, adjusting the center distance while ensuring adequate transmission space of the bogie power axle can effectively control the vibration of the axleboxes on both sides; The vibration response of the left axlebox is always larger than that of other positions under all working conditions, indicating that the side wheel and shaft far from the driving gearbox are more prone to encounter slackness failure induced by dynamic excitation. Therefore, during design stage, it is recommended to increase the axle interference fit.
March 5, 2026
Vibration Engineering
Research Article
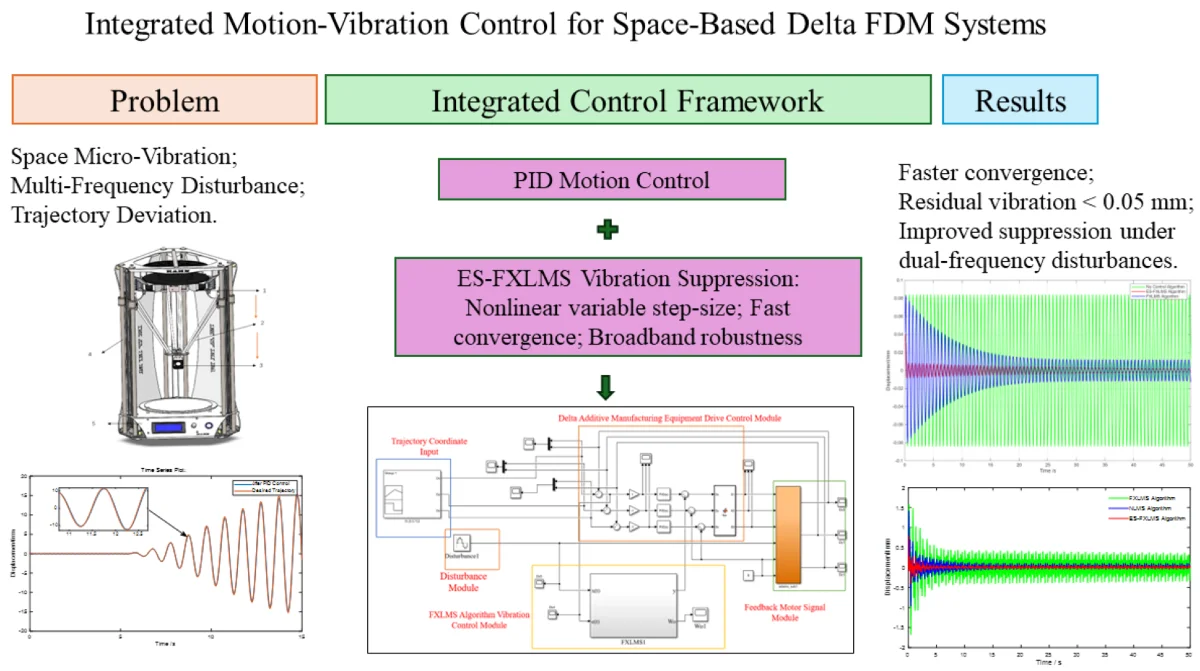
Research on integrated motion and vibration control methods for heated nozzles in space additive manufacturing equipment
In microgravity and disturbance-rich orbital environments, the thermal nozzle of Delta-type space-based fused deposition modeling (FDM) systems is prone to trajectory deviations and vibration-induced defects, which can severely degrade the surface quality and mechanical integrity of printed parts. To address this problem, an integrated motion-vibration control strategy is proposed. The motion loop employs a classical PID controller for accurate trajectory tracking, whereas the vibration loop adopts a Filtered-X Least Mean Square (FXLMS) algorithm with a nonlinear variable step-size scheme jointly modulated by exponential decay and sinusoidal functions. The proposed step-size mechanism improves convergence behavior and robustness under time-varying disturbances by enabling fast initial adaptation while maintaining stable steady-state performance. A high-fidelity ADAMS-Simulink co-simulation platform is developed for comparative evaluation. The results show that the proposed strategy reduces micro-vibration amplitudes, improves tracking accuracy, and provides stronger robustness than fixed-step adaptive approaches, thereby offering an effective solution for high-precision space-based additive manufacturing.
March 3, 2026
Informatics
Research Article
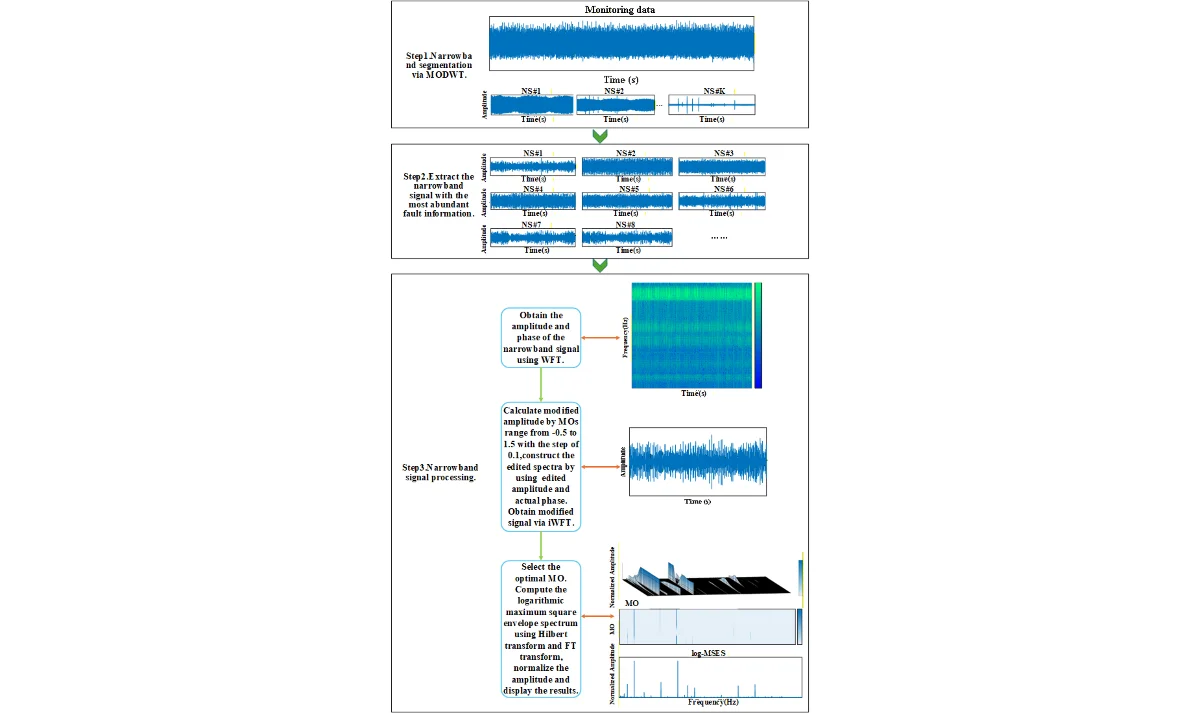
Fault diagnosis of rolling bearings based on amplitude modulation of local W transform spectrum
As one of the key components of transmission and support in rotating machinery, rolling bearings will directly affect the operating status of the equipment. Therefore, scholars have proposed various methods to process its fault signals. Among them, spectral amplitude modulation (SAM) is a nonlinear filtering method that can effectively extract bearing fault characteristics. However, due to the high-intensity noise interference in the working environment of the equipment, the interference component dominates the monitoring signal, and the fault characteristics are no longer obvious or even undetectable. To solve the above problems, this paper proposes a local W transform spectral amplitude (LWTSAM) modulation method. First, the method divides the original signal into multiple narrowband signals in different frequency bands and selects the narrowband signal with the most abundant fault information among them; then, the selected narrowband signal uses a windowed Fourier transform (WFT) to obtain the amplitude in the time-frequency domain, and uses different weight indices (MO) to correct the amplitude; Finally, the modified amplitude is combined with its original phase to perform inverse window Fourier transform to obtain the modified signal and its square envelope, and the square envelope under the optimal weight is calculated using unbiased autocorrelation and information entropy to complete the local W transform spectrum amplitude modulation. In this paper, this method is verified through fault data sets. The research results show that this method can effectively reduce the interference of noise on fault diagnosis, and the fault characteristic information obtained is clearer. Compared with SAM method, Autogram method and fast spectral kurtosis diagram method, the superiority of this method is proved.
February 28, 2026
Applied Mathematics
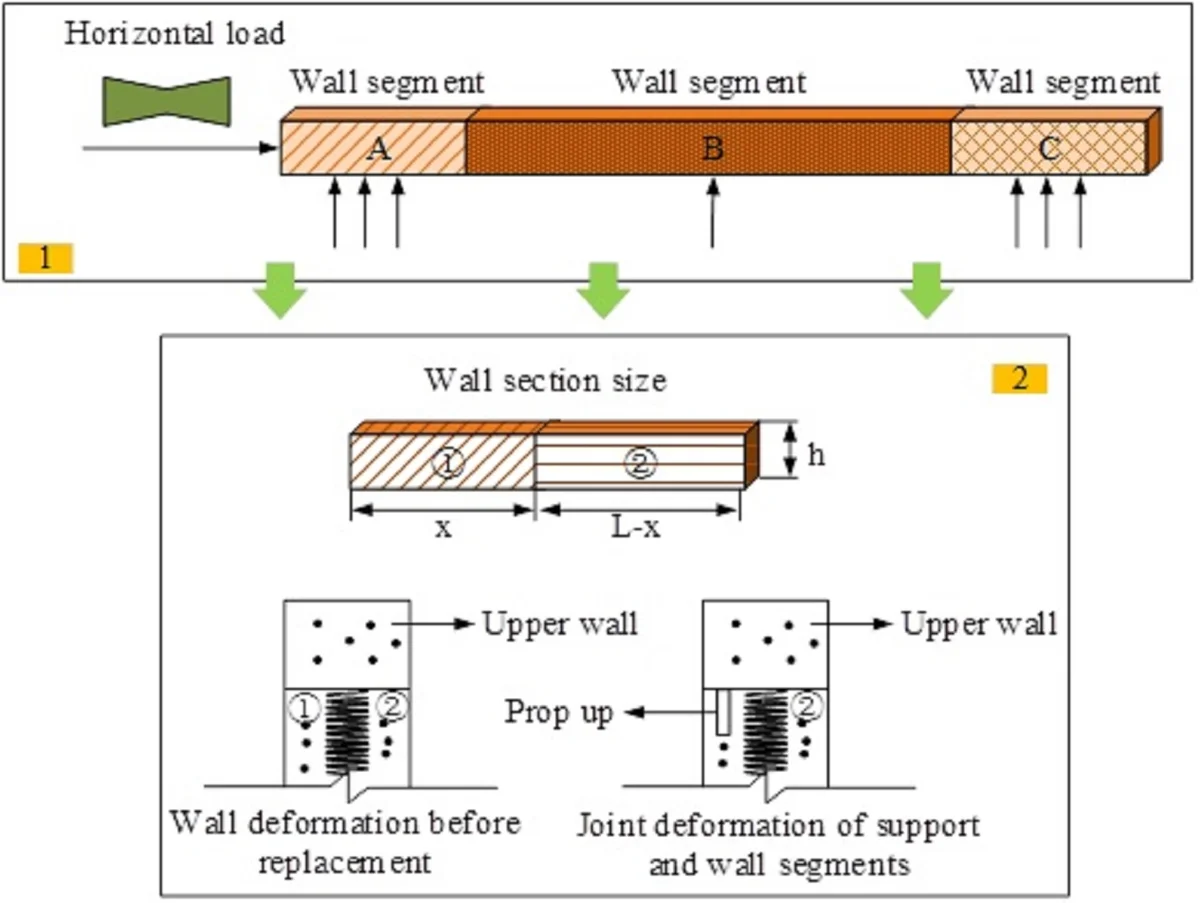
Research Article
Optimization of seismic performance of high-rise building shear walls based on partial replacement of concrete and steel pipe reinforcement
There are deficiencies in the optimization of the seismic performance of high-rise building shear walls, such as weak integrity and collapse resistance. Aiming at this problem, this study innovatively combines the partial replacement of concrete and steel pipe reinforcement technology, and proposes a method of locally adding steel pipe reinforcement shear walls. The experimental results showed that the specimens reinforced by the studied method exhibited better ductility and toughness when subjected to a vertical load of 840.84 kN as compared to the low-strength concrete specimens that were not reinforced by the studied method. The overall structure of the wall was able to maintain its load-bearing capacity despite the fact that the concrete at its base also suffered from crushing and spalling. In addition, the cracking displacement of the specimens (JGC-2, JGC-4, JGC-6) with localized steel pipe reinforcement was only 3.0 mm, 2.1 mm, 2.4 mm, respectively. The limit displacement was only 27.0 mm, 24.0 mm, 25.0 mm, and 45.0 mm, 47.0 mm, and 36.0 mm, respectively. The destructive displacement was only 45.0 mm, 47.0 mm, and 36.0 mm. The superiority of partial replacement of concrete and steel pipe reinforcement in improving the performance of high-rise building shear wall structures was further confirmed. It can be concluded that the research method can not only provide new ideas for the seismic strengthening of existing high-rise buildings, but also is expected to play an important role in a wider range of engineering applications. In turn, this will contribute to the improvement of the seismic performance of high-rise building structures and the protection of people's lives and property safety.
February 25, 2026
Vibration Engineering
Latest from engineering
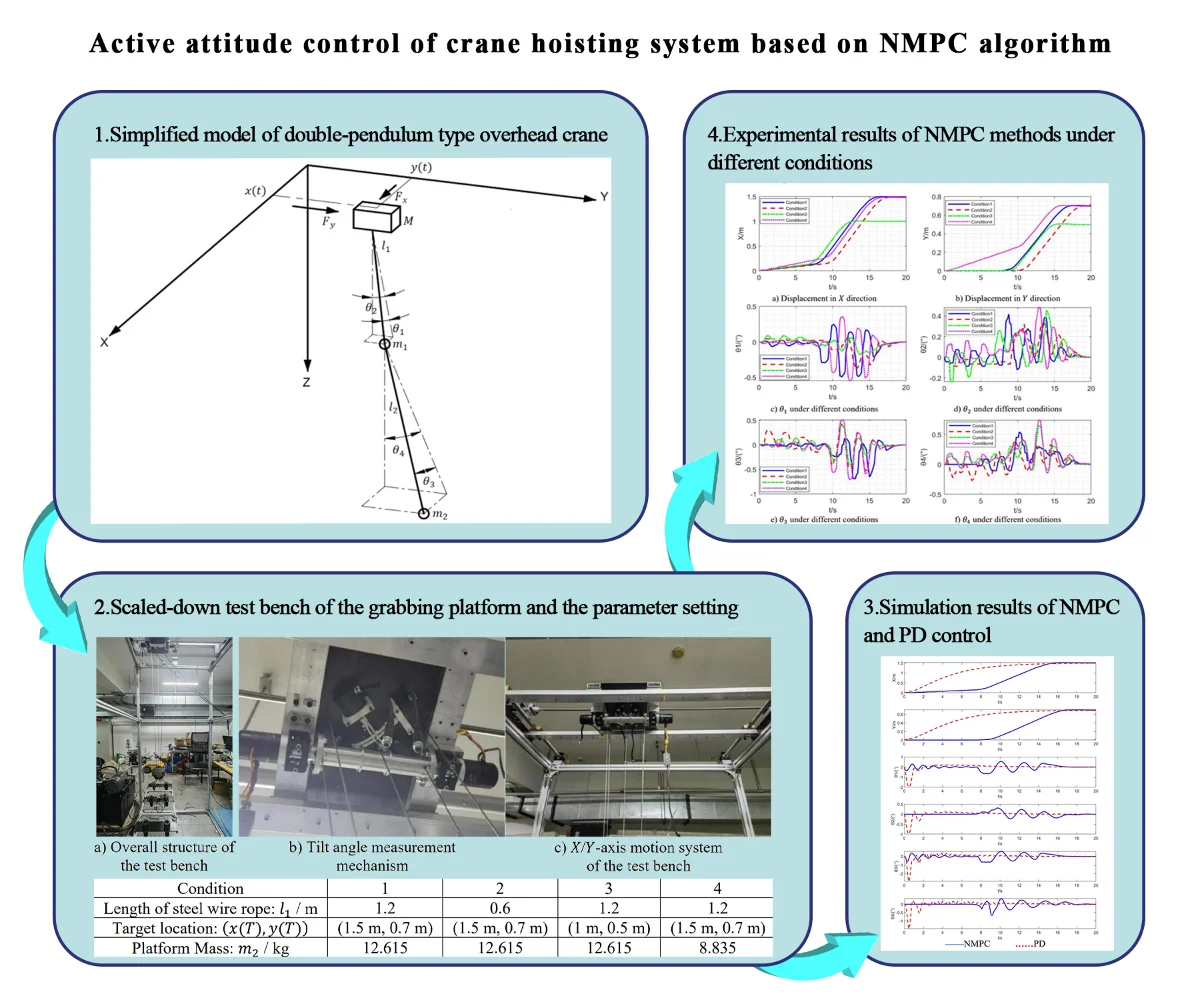
Research Article
Active attitude control of crane hoisting system based on NMPC algorithm
With the rapid development of construction industrialization, modular construction has been widely applied due to its advantages such as high efficiency and environmental friendliness. As the core hoisting equipment, the crane hoisting system faces issues like poor stability and low intelligence, which have become key technical bottlenecks restricting construction efficiency. To address the above problems, this study aims at the anti-swing control of the lifting and traveling mechanism, and establishes a dynamic model of the lifting and traveling mechanism with a double-pendulum effect. Based on this model, a nonlinear model predictive controller (NMPC) is designed, followed by simulation analysis and experimental verification. The simulation results show that the designed controller can effectively suppress the load swing during the movement of the trolley (the tilt angle is controlled within ±1°) and exhibits good robustness under different working conditions. In addition, by building a scaled-down experimental platform, the accuracy of the simulation model and the actual performance of the controller are further verified. This research provides an efficient and accurate hoisting solution for improving the precision and efficiency of tower crane systems in modular building construction, and is of great significance for promoting the development of modern construction technology.
February 21, 2026
Vibration Engineering
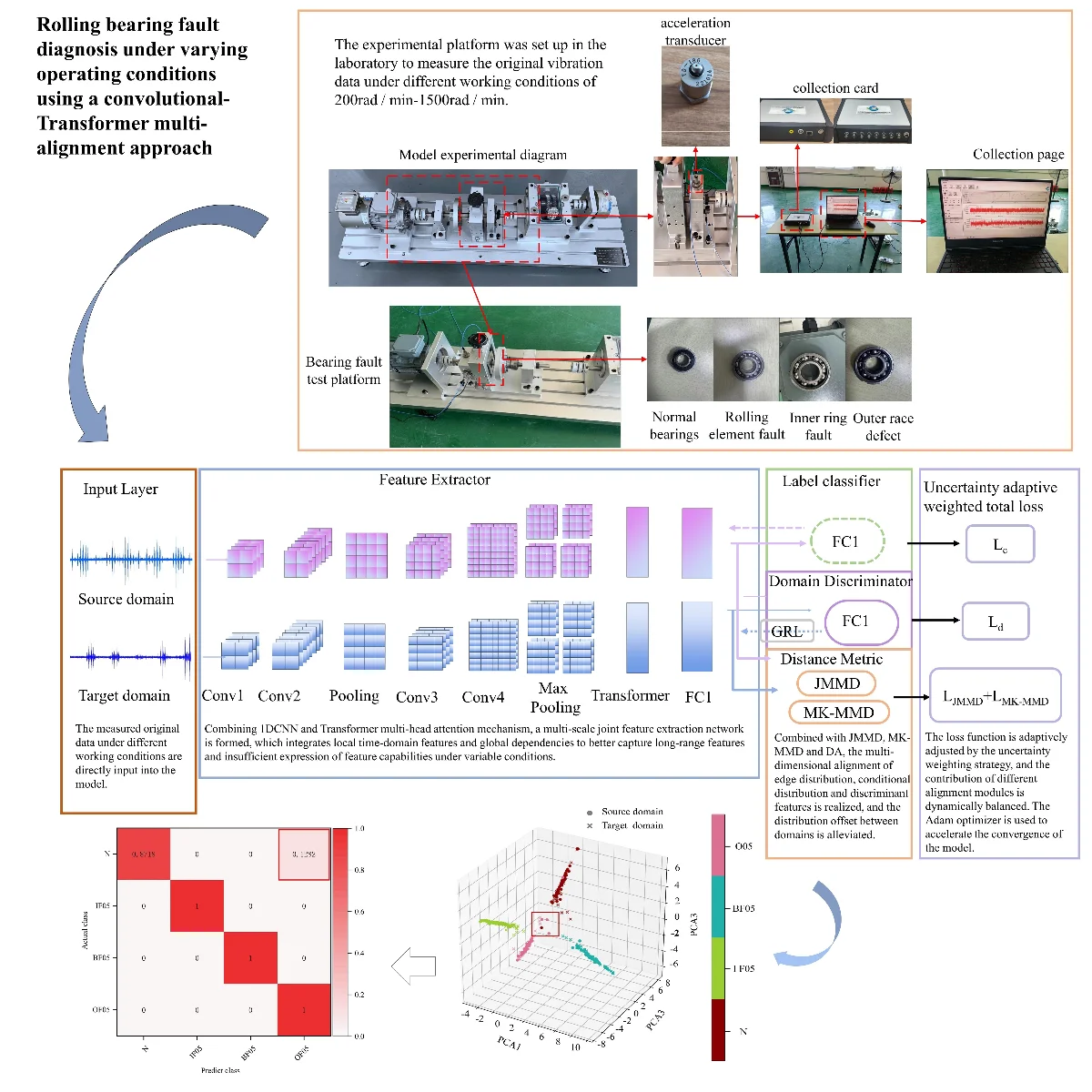
Research Article
Rolling bearing fault diagnosis under varying operating conditions using a convolutional-Transformer multi-alignment approach
In this study, a novel deep transfer learning method, termed the Universal Domain Alignment and Multi-level Alignment Network (UDAM-Net), is established to address the significant feature distribution discrepancy between the source and target domains caused by the difficulty of feature extraction for rolling bearings under complex operating conditions. In the feature extraction stage, a one-dimensional convolutional neural network is integrated with a Transformer-based multi-head attention mechanism to effectively enhance the feature representation capability of raw signals. Additionally, the complementary advantages of Joint Maximum Mean Discrepancy (JMMD), Multi-kernel Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MK-MMD), and a domain discriminator are explored by designing a collaborative mechanism combining distribution metrics and adversarial learning in conjunction with transfer learning. Furthermore, an uncertainty-based weighting strategy is introduced to adaptively adjust the loss function and dynamically balance the contributions of different alignment modules. Finally, the Adam optimizer is employed to accelerate model convergence. Experimental results on the CWRU public dataset and a laboratory-built test rig dataset demonstrate that UDAM-Net achieves classification accuracies of 96.67 % and 96.17 %, respectively. This study enlightens fault diagnosis based on feature extraction and cross-domain feature alignment.
February 21, 2026
Applied Mathematics
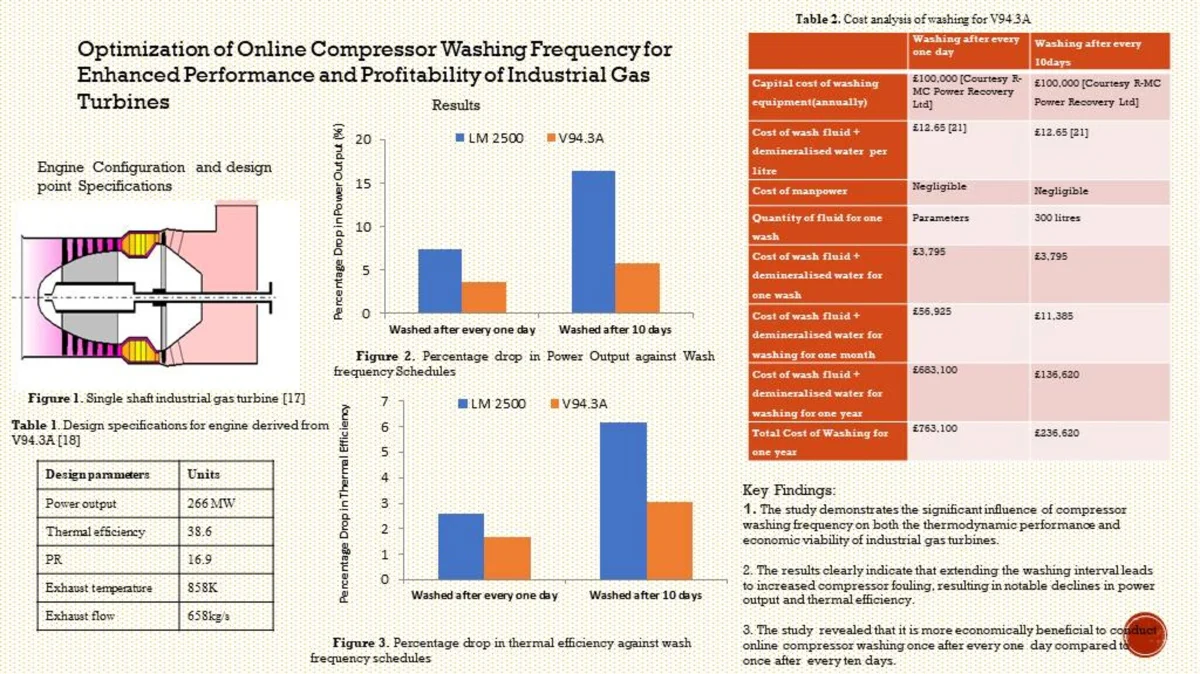
Research Article
Optimization of online compressor washing frequency for enhanced performance and profitability of industrial gas turbines
This study investigates the optimization of online compressor washing frequency for enhanced performance and profitability of industrial gas turbines. Two representative engines: an aero-derivative LM2500 and a heavy-duty V94.3A (also designated SGT5-4000F) were simulated in GasTurb software under varying washing intervals of one day and ten days. Experimental data were applied to model reductions in compressor isentropic efficiency and mass-flow capacity due to fouling. The results indicate that extending the washing interval from daily to every ten days for one year causes significant performance deterioration. For the LM2500, power output decreased from 7 % to 16 %, thermal efficiency from 2.6 % to 6 %, and heat rate rose from 2.7 % to 6.6 %. Corresponding changes for the V94.3A were smaller, confirming that the aero-derivative turbine is more sensitive to fouling than the heavy-duty unit. Economic evaluation showed that while more frequent washing increased wash fluid consumption and operational costs, it provides substantial financial benefits. Daily washing produced additional annual net profits of approximately £11.69 million for the V94.3A and £4.6 million for the LM2500 compared with ten-day intervals. Overall, the findings demonstrate that optimizing compressor washing frequency is essential to sustain turbine performance, improve fuel efficiency, and maximize profitability. Frequent online washing mitigates the adverse effects of fouling and ensures cost-effective, reliable, and energy-efficient gas-turbine operation.
February 19, 2026
Informatics
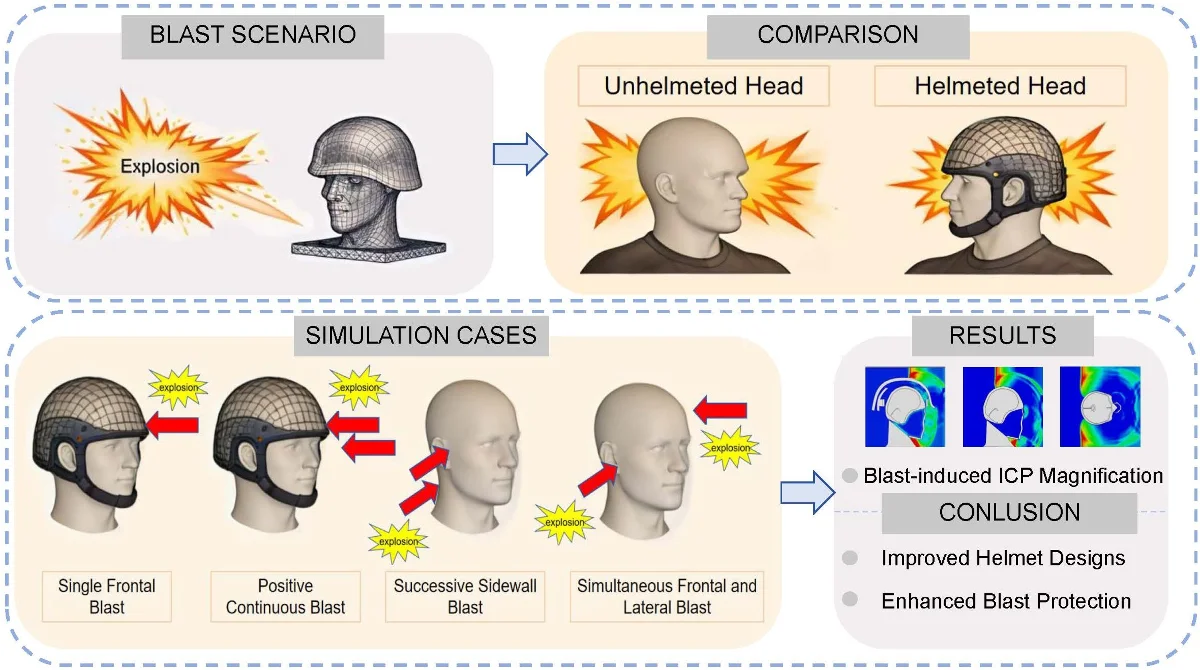
Research Article
Study on craniocerebral dynamic response and helmet protection performance under accompanying shock wave
To systematically investigate the protective effects of helmets against human head injuries under various shock wave conditions, a finite element head-helmet coupling model was developed. This model analyzed how helmets influence biomechanical response parameters, such as intracranial and cranial pressure, when subjected to a single blast wave and its accompanying shock wave. While extensive research exists on single blast scenarios, studies on the more complex and militarily relevant accompanying shock waves, which pose a greater threat due to prolonged loading and multiple reflections, remain scarce. Several impact scenarios were considered, including single frontal impact, positive continuous impacts, successive sidewall impacts, and simultaneous frontal and lateral impacts. The study examined the dynamic changes in brain tissue within a blast environment to assess the efficacy of helmets in protecting the human head. In single frontal impact scenarios, helmets effectively reduced intracranial pressures in the frontal, occipital, and parietal lobes by 32 %, 38 %, and 19 %, respectively, while significantly decreasing the stress peak at the back of the skull. During positive continuous impacts, helmets decreased intracranial pressure in the parietal and occipital lobes by 36 % and 21 %, respectively, although their effectiveness in reducing frontal lobe pressure was limited due to inadequate facial protection. For successive sidewall impacts, helmet protection delayed the blast wave, reducing intracranial pressure in the frontal lobe by 60 kPa but increasing pressure in the parietal lobe by 80 kPa. This alleviated stress on the skull’s rear while increasing stress on the opposite side. In scenarios involving simultaneous frontal and lateral impacts, lateral blasts increased parietal intracranial pressure by 20 kPa, with the right hemisphere experiencing more pressure than the left due to the mitigating effect of reflective side blasts on skull stress. The study found that, compared to single blast waves, accompanying shock waves present a greater risk of cranial injuries due to their prolonged impact. These findings address a critical gap in blast neurotrauma research and provide valuable insights into the biomechanics of head injuries under realistic multi-blast conditions, which can directly inform the design of improved helmets with enhanced protection in complex blast environments. However, because shock waves may originate from multiple directions and elevations, the protective capability of conventional helmets for the facial region remains limited.
January 11, 2026
Mechanical Engineering
Recently published
Research article
January 9, 2026
Multi-scale rheological properties of municipal solid waste fly ash-asphalt mastic materials
By Weili Chen
Recently published
Research article
December 29, 2025
Maintenance, repair, and overhaul of robotic systems
By Guilherme E. Vieira, Jeffrey W. Herrmann
77th International Conference on VIBROENGINEERING
Advanced Engineering Problems in Mechanical, Civil, Communication, and Autonomous Technologies
Date
June 11-12, 2026
Submission deadline
4/15/2026 11:55:00 PM
Conference format
Hybrid
Best of engineering
Editor's pick
Research article
December 22, 2025
Experimental and finite element analysis of the structural durability of special self-propelled rolling stock frames
By Izzatillo Raxmiddinov, Sherzod Fayzibaev, Yusufov Abdulaziz, You Taiwen, Khusan Kosimov, Nusratillo Abdullayev
Editor's pick
Research article
December 20, 2025
Design of a composite repetitive controller for grid-connected inverters with a notch filter
By Fen Liang, Xiao Liang, Huanke Cheng, Ho-Joon Lee
Editor's pick
Research article
October 31, 2025
Application of GSABO-VMD-KELM in rolling bearing fault diagnosis
By Qiang Li, Chao Wu, Qing Lv, Jin Wang
Editor's pick
Research article
September 30, 2025
Modernization of the electromagnetic vibration stand for testing aviation industry products
By Ivan Kolodiy, Oleksii Lanets, Pavlo Maistruk, Iryna Derevenko, Ihor Nazar, Ivan Khomych
You might also like
Most downloaded
Research Article
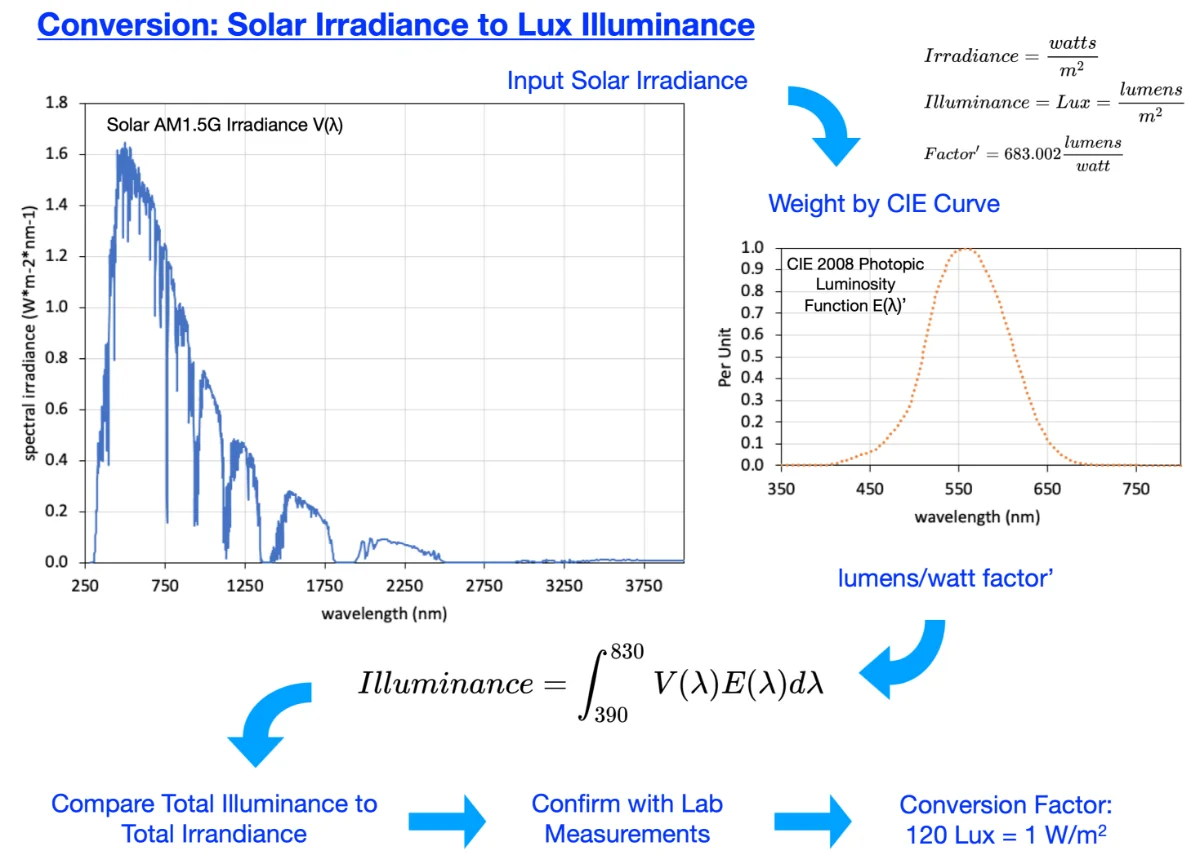
A conversion guide: solar irradiance and lux illuminance
By Peter R. Michael, Danvers E. Johnston, Wilfrido Moreno
The standard for measuring solar irradiance utilizes the units of watts per meter squared (W/m2). Irradiance meters are both costly and limited in the ability to measure low irradiance values. With a lower cost and higher sensitivity in low light conditions, light meters measure luminous flux per unit area (illuminance) utilizing the units of lumens per meter squared or lux (lx). An effective conversion factor between W/m2 and lx would enable the use of light meters to evaluate photovoltaic performance under low solar irradiance conditions. A survey of the literature found no definitive and readily available “rule of thumb” conversion standard between solar irradiance and illuminance. Easy-to-find Internet sources contain conflicting and widely varying values ranging from 688449 to 21000 lx for 1000 W/m2 (1 Sun) of solar irradiance. Peer-reviewed literature contains Luminous Efficacy equivalent values ranging from 21 to 131 lx per W/m2. This manuscript explores the relationship and establishes a theoretical and laboratory measurement guide for the conversion between solar irradiance and illuminance. The conversion factor includes standards data, equipment calibration accuracy, and uncertainty estimates. Solar Irradiance of 1 Sun (1000 W/m2) for an LED-based solar simulator is (116 ± 3) klx and (122 ± 1) klx for outdoor sunlight.
December 4, 2020
Applied Physics
Most downloaded
Research Article
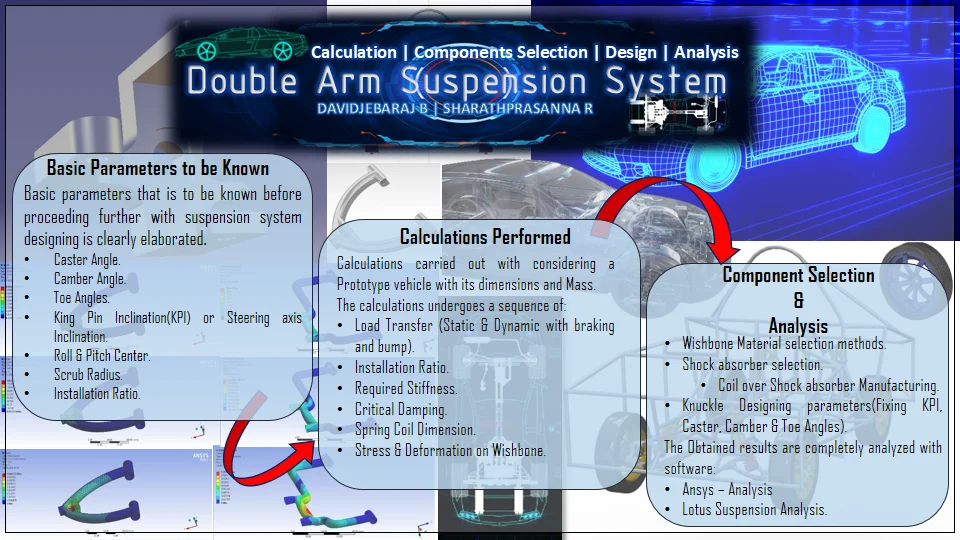
Design and calculation of double arm suspension of a car
By David Jebaraj B, Sharath Prasanna R
Suspension system is one of the challenging portions in designing a vehicle. The complete stability of the vehicle under dynamic conditions depends on the suspension system of the vehicle. Suspension system of a vehicle is interlinked with other systems such as steering, Wheels and Brakes. The main objective of this document is to provide complete guidance in designing and calculation of an independent suspension system with double control arms. The required parameters are calculated on considering a prototype vehicle with gross weight of 350 kg such as required stiffness of shock absorbers, Ride frequency, Motion ratio, Coefficient of damping etc. A CADD model was made with CATIA v5 r20 and SOLIDWORKS on the basis of calculations obtained and stress analysis was carried out for this model in various software such as Ansys. The complete assembled model was tested in LOTUS Shark and the result was obtained.
June 30, 2020
Industrial Engineering
Modal finite element analysis of PCBs and the role of material anisotropy
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are epoxy resin-impregnated and cured sheets of counter woven glass fabric (e.g. FR4) laminated between thin sheets of Copper. The nature of the PCB is inherently anisotropic and inhomogeneous but previous modal FEMs of PCBs have assumed isotropic, anisotropic (transversely isotropic and orthotropic) material properties and shown good correlation with test data for specific scenarios [1-3]. This paper details part of a research program aimed at gaining a better understanding of accurately modeling PCB’s dynamic behavior. New investigations into the impact of material anisotropy and, in particular, the effect of material orthogonal plane definition (Ex and Ey) on eigenfrequencies is analysed. A modal FEM of a JEDEC PCB is created, verified, and validated using well established theories by Steinberg and empirical data by others [4, 5]. The relative contributions of Ex, Ey and Ez on PCB eigenfrequencies is examined using a parametric modal FEM, analysing the role of material isotropy verses anisotropy. The impact of transversely isotropic material properties is also analysed for a typical JEDEC PCB. This analysis details the mesh density required for accurately modeling the PCB eigenfrequencies. The results show that a 100 % increase in Ez has only a 0.2 % difference in the eigenfrequency where as a 100 % increase in Ey has a 1.2 % difference in the eigenfrequency. The effect of orthotropic plane definition (alternating Ex with Ey) on the JEDEC PCB amount to a 7.95 % delta in eigenfrequency.
Coilgun design and evaluation without capacitor
Capacitors with high voltage and capacity values are used in most induction coilguns that are designed and constructed. The fact that capacitors are quite bulky and slow in energy transfer and how a coilgun can be made without using capacitors is the study subject of this article. Two and four coil gun samples were made to find the essential components of an electric gun, and the results are reported in this article. The accuracy of the results is also confirmed by FEMM analysis for these models. The harmony of experimental and theoretical results shows that smaller and low cost portable electrical weapons can be a powerful alternative to firearms in the future.