Health Sciences Research
Editor's pick
Research Article
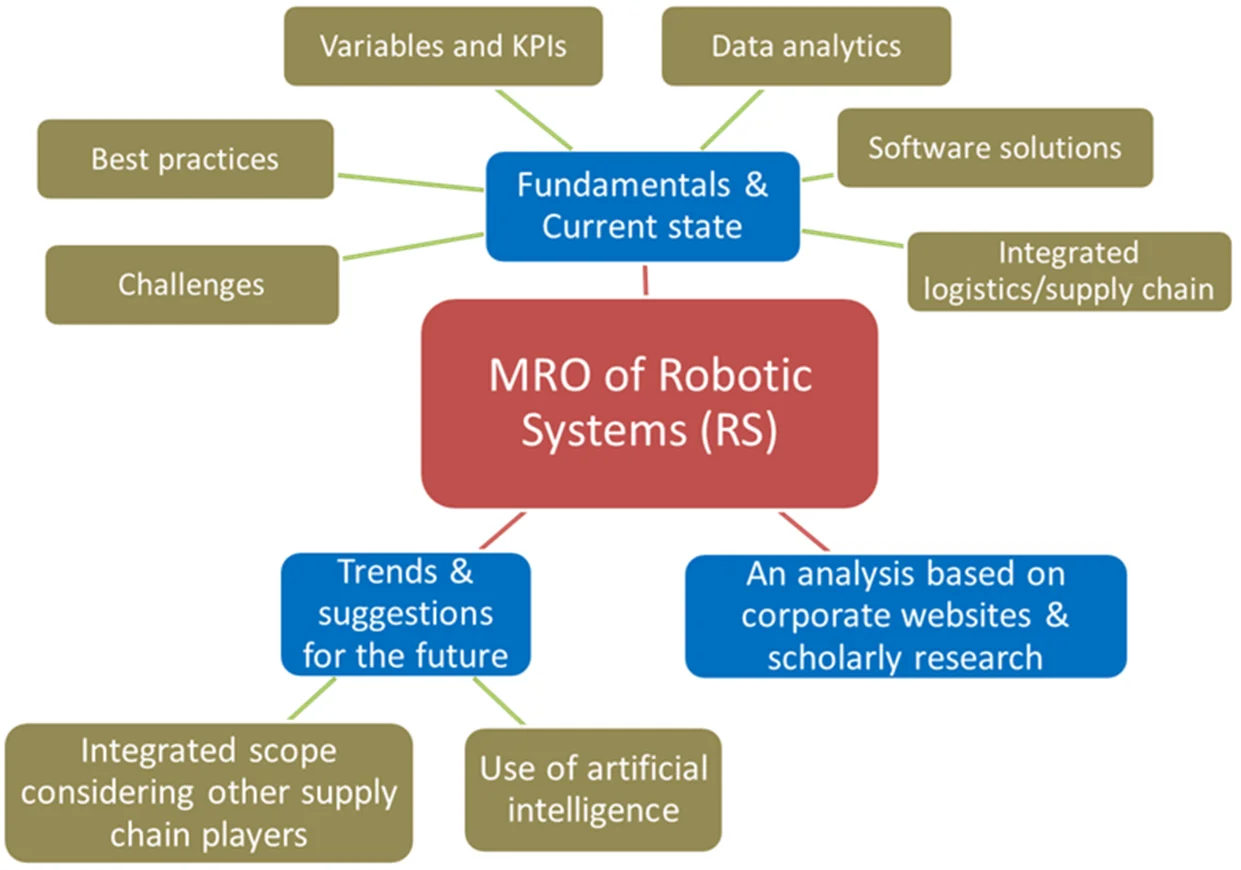
Maintenance, repair, and overhaul of robotic systems
By Guilherme E. Vieira, Jeffrey W. Herrmann
This paper not only explores the fundamental aspects of but also brings new ideas for maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) operations of robotic systems (RS). This synthesis is based on the limited scholarly research in this area and on information gathered from comprehensive web searches and analysis of corporate websites so that the results reflect the current views of RS developers and operators. The paper describes several crucial areas concerning RS MRO: maintenance of robotic systems, challenges and best practices for RS MRO, predictive maintenance variables and key performance indicators, data analytics, software solutions for RS MRO, and logistics/supply chain approach that should be considered. These insights provide not only a comprehensive understanding of the current state of RS MRO but also describe trends and suggestions for the future of RS MRO, emphasizing the novelty of the proposed research conducted. Key trends that organizations will need to address include the use of artificial intelligence (AI) models and the increasing importance of RS MRO logistics and supply chain management.
December 29, 2025
Biomechanics
Most cited
Research Article
A portable breast cancer detection system based on smartphone with infrared camera
By Jian Ma, Pengchao Shang, Chen Lu, Safa Meraghni, Khaled Benaggoune, Juan Zuluaga, Noureddine Zerhouni, Christine Devalland, Zeina Al Masry
September 26, 2019
Biomechanics
Most cited
Research Article
Three-dimensional reconstruction of medical images based on 3D slicer
By Xiaolin Zhang, Kexin Zhang, Qiuling Pan, Jincai Chang
June 30, 2019
Public Health
Most cited
Research Article
Modern biophysical view of electromagnetic processes of the phenomenon of life of living biological systems as a promising basis for the development of complex medicine: the role of biophotons
By Ganna Nevoit, Inga Arune Bumblyte, Maksim Potyazhenko, Ozar Minser, Alfonsas Vainoras
June 25, 2023
Public Health
Most cited
Research Article
Applications of collaborative robots in agile manufacturing: a review
By Siddhant Kakade, Bhumeshwar Patle, Ashish Umbarkar
June 26, 2023
Biomechanics
Jaw Functional Orthopedics and Craniofacial Growth
Research Article
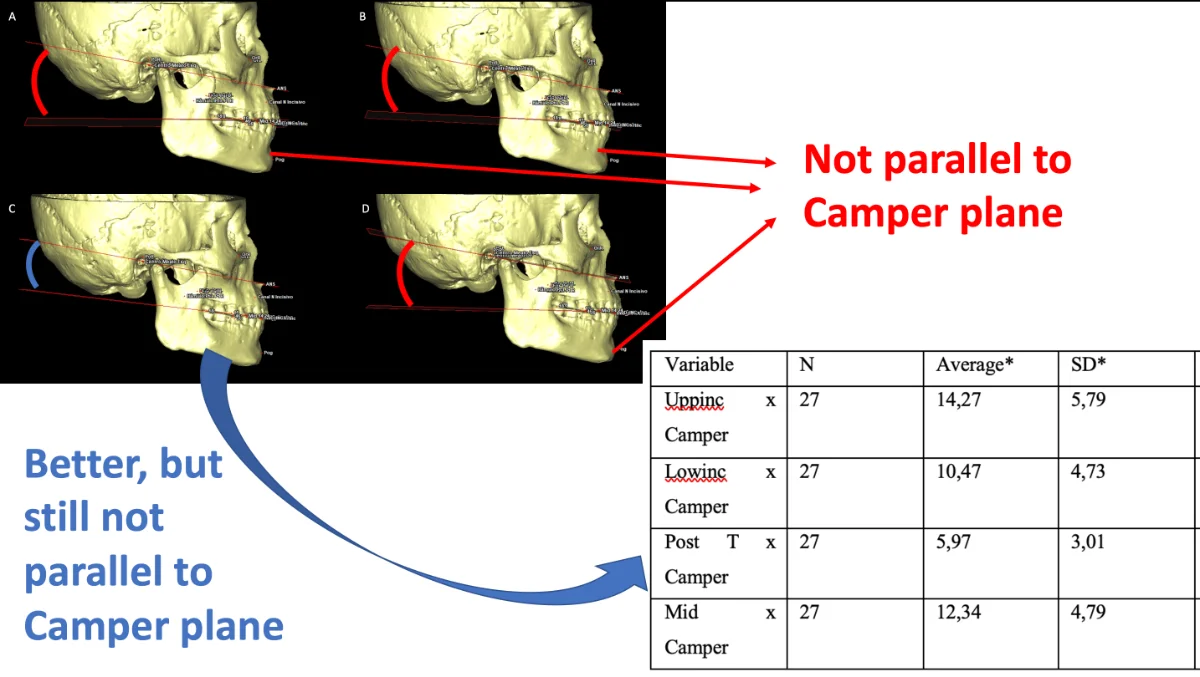
Occlusal plane parallel to camper plane: reality or fallacy? A tomographic study on human Sambaqui skeletal remains
Introduction: Since long time ago, dentists had used parallelism with Camper plane as a reference to establish a correct occlusal plane. However, in the literature, there are several different landmarks used to trace the occlusal plane and there are also many researchers questioning this parallelism. To evaluate it, we used ancient skulls from Human Sambaqui skeletal remains. The authors choose an ancient population because they were submitted to same environmental conditions, avoiding bias in craniofacial growth epigenetic stimuli. Methodology: For this work we analyzed tomographies of 27 well preserved adult skulls. The program used was Vista Dent Pro 2.1. Camper plane was determined according to the original points described by Peter Camper. We used the four occlusal planes more cited in the literature. Results: None of the occlusal planes evaluated on this study, showed parallelism with Camper plane. The occlusal plane determined by posterior teeth was the one that showed less divergence but still with a high SD and mediana. Conclusion: In Sambaqui ancient population, Camper plane was not a reliable reference to trace occlusal plane. It is necessary further investigations to find a better reference for prosthetic, orthodontic, functional orthopedics or orthognathic surgery purpose.
June 30, 2022
Orthopedics
Research Article
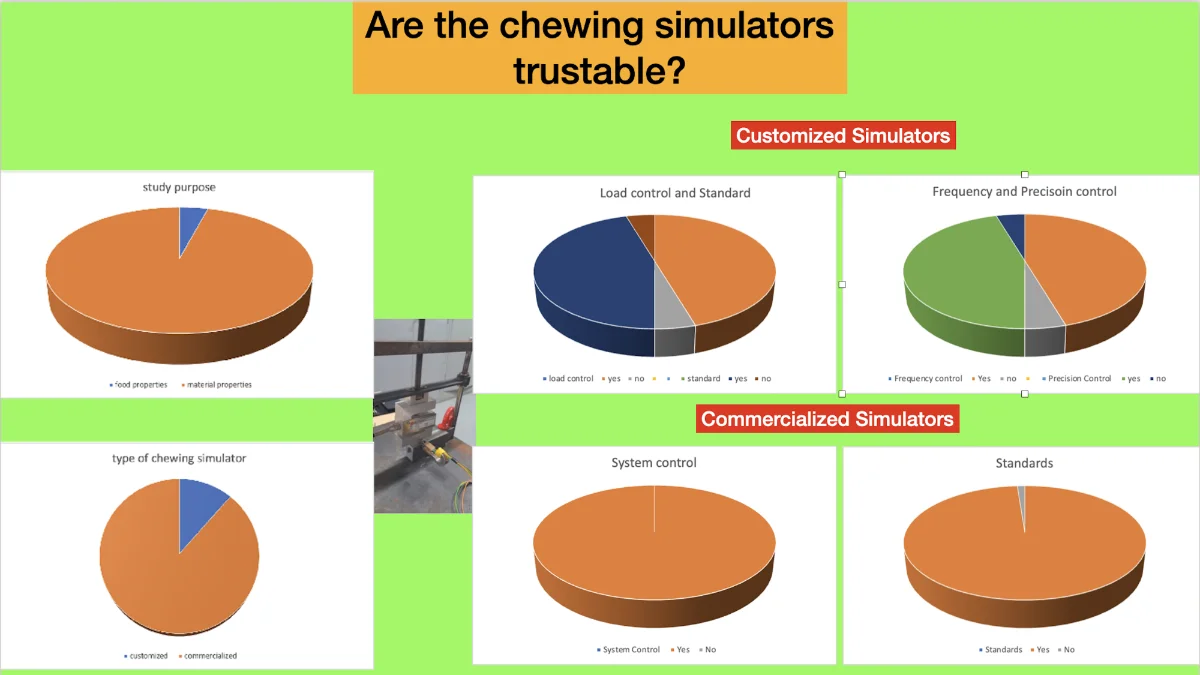
Do chewing simulators influence the test results of dental materials? Systematic review
Investigate whether different results about the physical properties of the same biomaterial frequently found in the literature are due to chewing simulator deficiency. A literature review was performed by searching for data on indicators of test accuracy, reproducibility, maintenance of test parameters during all experiments, and standards in the articles or in the sites of manufacturers. The database searched was CAPES PORTAL, and the keywords used were “bite force” AND “simulator”, “chewing simulator” and “mastication simulator”. Including criteria for the papers are publication filter date of “January 1, 2016”, articles in English, Spanish and Portuguese language were accepted. The first 100 papers that seemed suitable when considering the title and abstract were recovered. Only one simulator used for food property studies had the parameters searched. In the customized simulators for biomaterial properties, only one showed standards, and 8 showed all other parameters searched. All manufactured simulators showed all parameters searched, and only two manufactures did not show standards. Based on the data obtained, the disparate results of experiments with dental materials appeared to be more related to the test conditions than to the testing machines. Knowledge Transfer Statement The findings of the current review suggest that the chewing simulators used in preclinical research are reliable, bringing safety to restorative processes regarding the material. Any difference in preclinical investigations about dental material physical properties is due to test conditions other than chewing simulators.
June 25, 2023
Orthopedics
Research Article
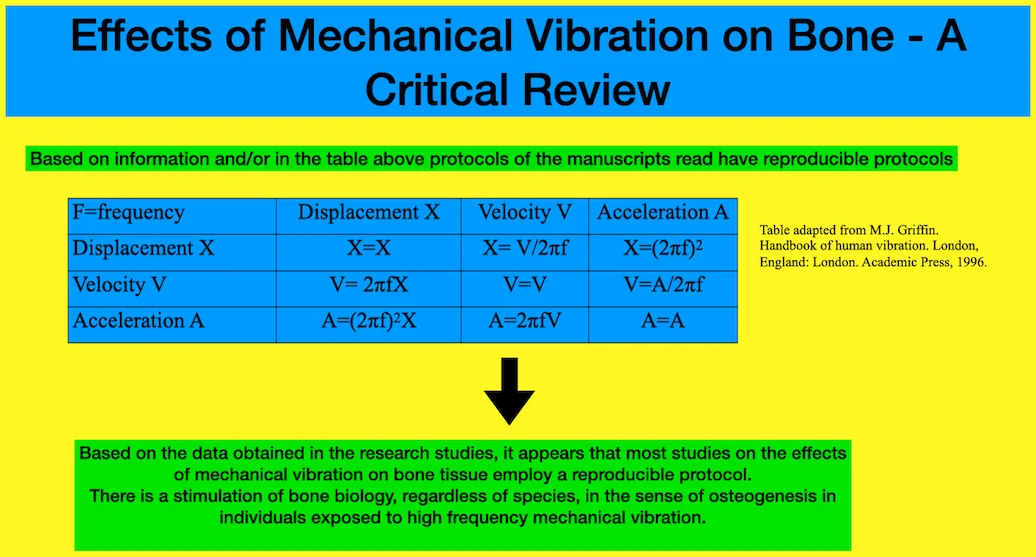
Effects of mechanical vibration on bone – a critical review
The benefits of reduced treatment time and comfort for patients undergoing corrective dental treatment with devices gave rise to the creation and modification of long-standing treatment protocols. One of the protocols used for these purposes is mechanical vibration. Objective: This review aimed to study the effects of mechanical vibration on bone. Methods: Portal Capes (periodicos.capes.gov.br) database was searched using the keywords “vibration” and “bone” with no date limit. Based on the title and abstract, the first 50 relevant studies were retrieved. The measured frequencies were between 4 and 150 Hz. Regarding exposure time and the number of applications, the variation is so wide that the average or median would not represent a realistic sample pattern. Results: In the retrieved studies, 41 reported improvements in bone conditions. Research studies show that a reproducible protocol is being applied in most studies on the effects of mechanical vibration on bone tissue. Conclusion: There is stimulation of bone biology, regardless of species, in the sense of osteogenesis in individuals exposed to high frequency mechanical vibration. To improve research protocols on the effects of vibrations on the body, more studies are needed.
November 28, 2022
Orthopedics
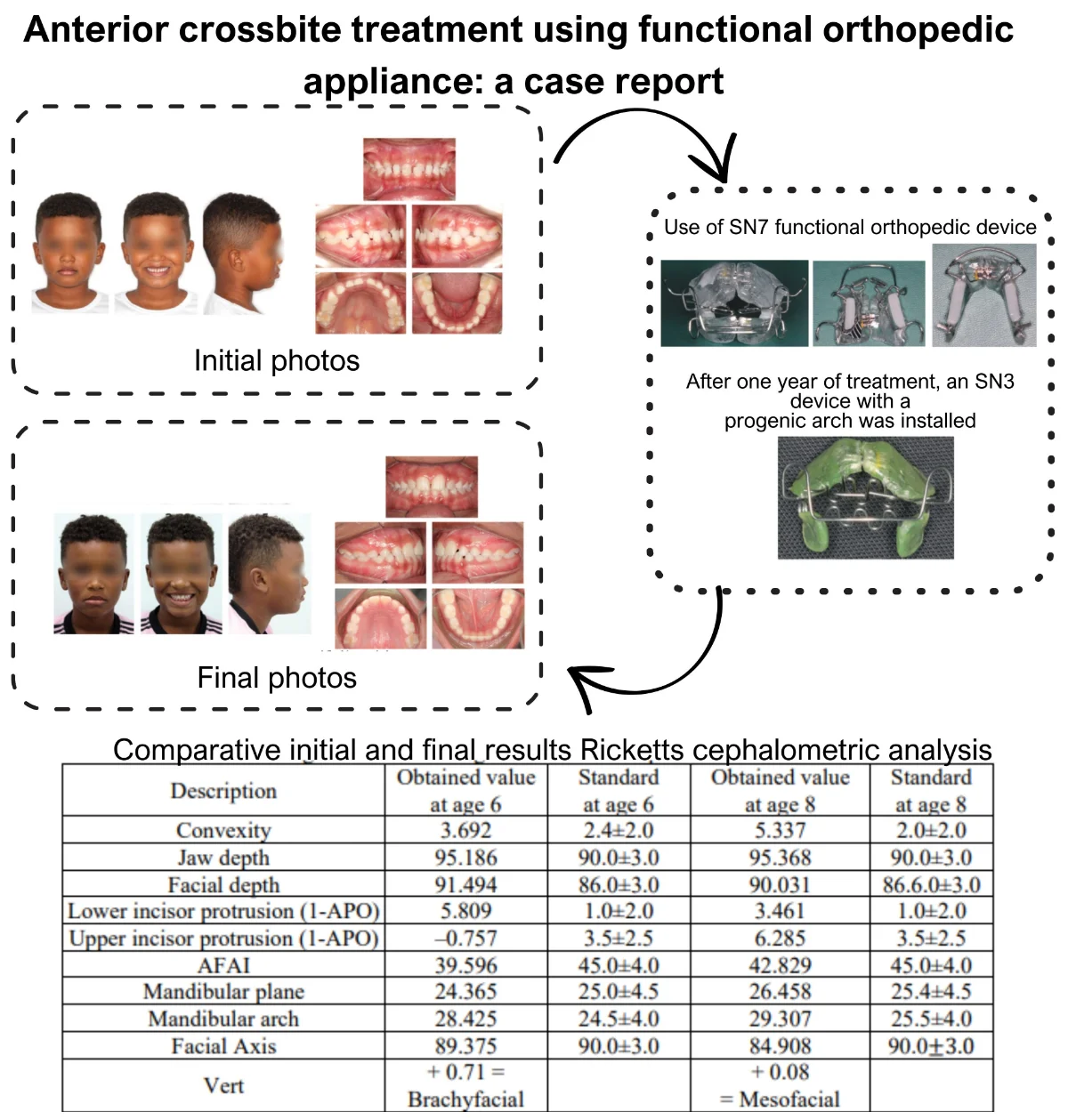
Research Article
Anterior crossbite treatment using functional orthopedic appliance: a case report
Anterior crossbite can affect primary, mixed, and permanent dentitions. Early treatment is recommended, as it can impact facial, aesthetic, functional, and developmental aspects. The etiology of anterior crossbite is multifactorial, including dental, skeletal, and postural origins. Treatment should be defined based on age and etiology, with various therapeutic resources available for correction. In primary dentition, direct flat tracks, different types of functional orthopedic appliances, quad-helix, and facial mask can be used. In mixed dentition, fixed segmented or continuous orthodontics, elastics, and other devices can be added to the treatment. In permanent dentition, orthognathic surgery may be indicated for adults, especially in cases of anterior crossbite associated with skeletal Class III that cannot be compensated dentally. This case report describes the treatment of early mixed dentition anterior crossbite with a functional orthopedic appliance at the Orthodontic Specialization, Postgraduate Course at Modal college, Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, Brazil. After correction, proper chewing functions were reestablished with ideal developmental stimuli.
June 28, 2023
Orthopedics
Jaw Functional Orthopedics and Craniofacial Growth
<p>Original scientific articles presenting information that is new and relevant to jaw functional orthopedics</p>
APC
Free of charge
Best of Theme
Most cited
Research article
September 26, 2019
Study of CO2 emissions from energy consumption in Spanish hospitals
By Justo García-Sanz-Calcedo
Most cited
Research article
August 11, 2021
Positioning algorithm for AGV autonomous driving platform based on artificial neural networks
By Patryk Bałazy, Paweł Gut, Paweł Knap
Most cited
Research article
June 30, 2020
Brain CT image segmentation based on 3D slicer
By Yuxuan Wang, Han Wang, Keqin Shen, Jincai Chang, Jianzhong Cui
Most cited
Research article
May 15, 2020
Hybrid artificial genetic – neural network model to predict the transmission of vibration to the head during whole-body vibration training
By M. Alshabi, N. Nawayseh, M. Bettayeb
You might also like
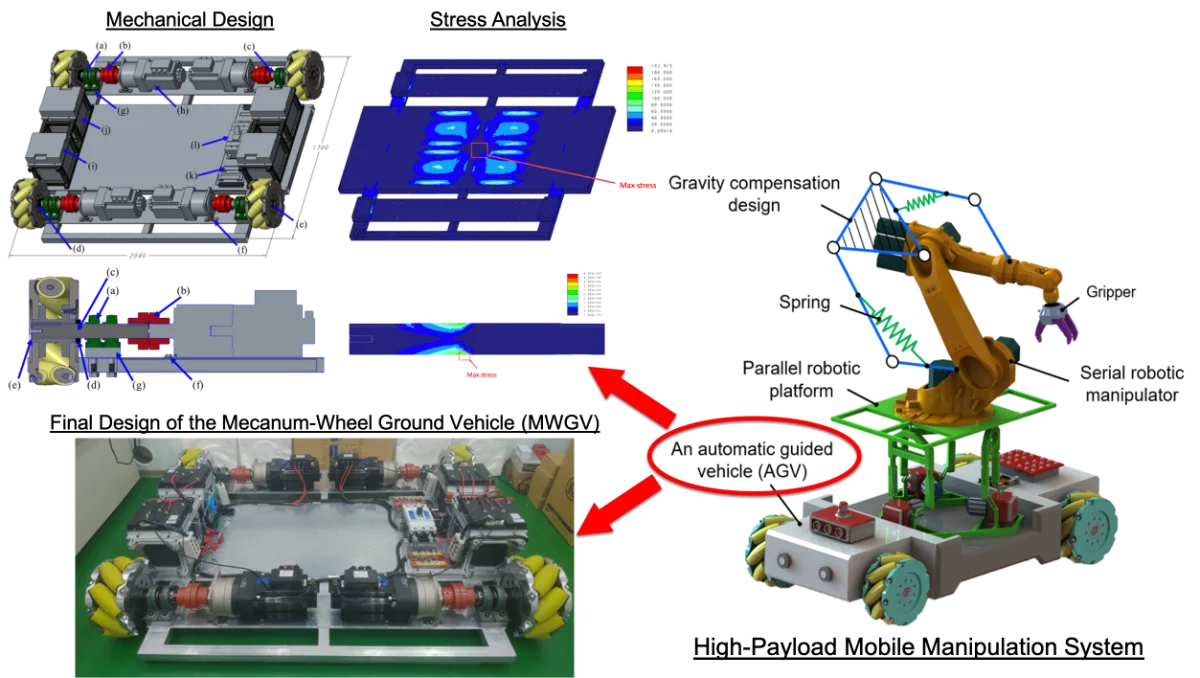
Most downloaded
Research Article
Design of a high-payload Mecanum-wheel ground vehicle (MWGV)
By Zi-Yin Chen, Pei-Ren Liaw, Vu Linh Nguyen, Po Ting Lin
With the rapid developments of Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing, customized manufacturing has been becoming greatly needed. Meanwhile, the challenge of production automation has become more bigger, especially for the automation of moving, picking, placing and manipulating objects. Many researchers have begun to work on Autonomous Ground Vehicles (AGVs). Most AGVs were utilized to carry middle or small objects, as the high-payload AGVs were rarely developed. This paper focused on the design of a High-Payload Mecanum-Wheel Ground Vehicle (MWGV), which was 1.7 m wide and 2.04 m long. The weight of the vehicle was 740 kg and it was able to carry the payload as its own weight (i.e. around 7,300 N). The safety factor of the structural strength was greater than 1.66 and the safety factor of the axial design was at least 6.24. The vehicle was designed to carry 150-kg weight with a reach of 1.375 m without falling. The design of Mecanum wheels provided great flexibility on movement with small rotational radius. Mathematical descriptions about how Mecanum wheels were controlled was also introduced in this paper. Furthermore, the mechatronics and software integrations were demonstrated. The final experimental results showed the developed MWGV was able to perform the desired movement properly.
June 30, 2021
Biomechanics
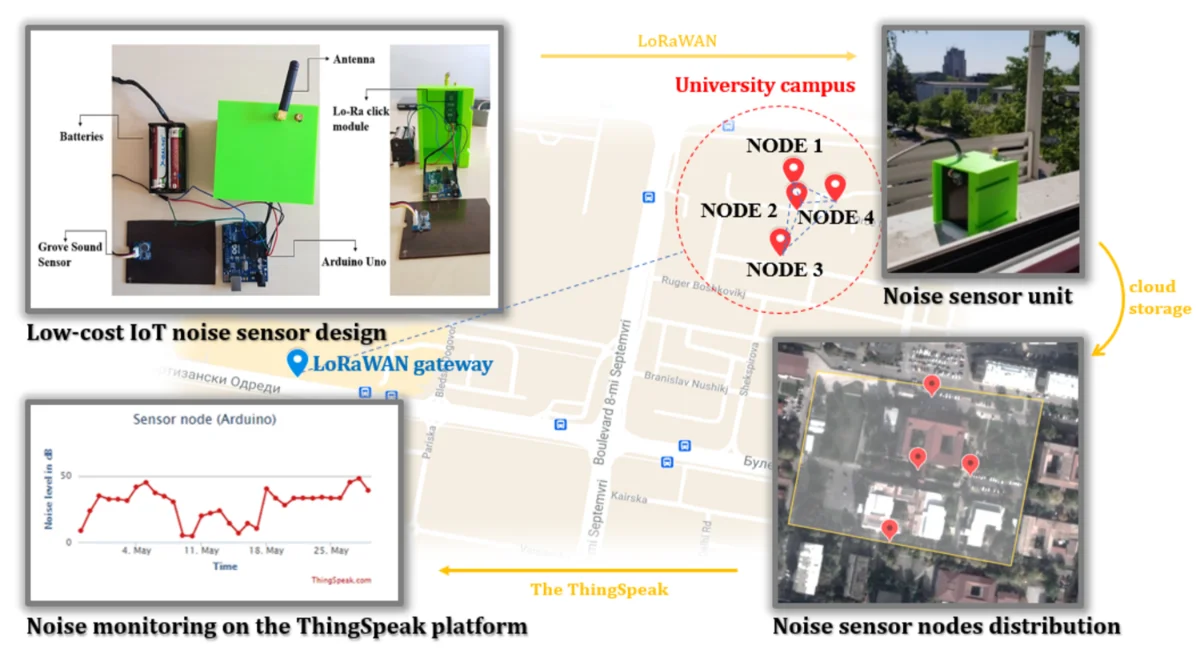
Most downloaded
Research Article
Design of low-cost wireless noise monitoring sensor unit based on IoT concept
By Maja Anachkova, Simona Domazetovska, Zlatko Petreski, Viktor Gavriloski
The recent expansion of wireless sensor networks (WSN) in urban cities has led to possibility of generation of large amounts of information data from the environmental monitoring systems among which one of the most concerning is the excessive urban noise pollution. As opposed to the conventional noise mapping procedures that involve costly and time-consuming measurement process with a traditional high-priced noise level meter, the low-cost wireless sensor networks provide a method for achieving data collection and analysis with a higher level of granularity. Тhis paper presents a wireless noise sensor unit design for continuous environmental noise level monitoring as a framework for the realization of the Internet of Things (IoT) and „Smart city” concept. The concept involves the complete noise data information system, from sensor structure to data visualization and data analysis. The overall design, characteristics and performance of the sensing system for continuous measuring urban noise pollution is discussed.
January 22, 2021
Public Health
Effect of heat transfer optimization on brake noise characteristics of automotive disc brake
Heat effect is one of the most important factors affecting the brake noise level. The finite element model for transient heat transfer analysis of disc brake is established based on heat transfer control equation and heat dissipation boundary conditions of dynamic convection. According to the NVH test and modal calculation, the brake noise characteristics are tested and analyzed. Meanwhile, the heat transfer simulation is verified and shows high accuracy. The discrete data for the response surface function are obtained by the Central Composite Design method with the peak temperature and mass as the target variables. The error of regression function is judged by fitting decision coefficient, correcting decision coefficient and root mean square error. By the optimizing mathematical model, the brake disc temperature peak can be greatly reduced and the heat transfer ability is obviously optimized without mass increasing, the time with temperature above 120 °C can be reduced by 46 %. Through the comparison of brake noise level before and after optimization, it can be known that the noise level can be significantly decreased after structural optimization, except the first order resonance frequency. The optimization result has good social and economic value.
Experimental and finite element approach for finding sound absorption coefficient of bio-based foam
The enormous consumption of Polyurethane foam leads to severe environmental pollution and health hazards, so it is necessary to overcome this problem. This paper presents alternative and less hazardous foam that differs from traditional foams. A bio-based foam was developed either by using castor oil-based polyol or natural fibers as fillers. In the present study, rigid foam is synthesized by both castor polyol and luffa fiber, whereas for flexible foam, only luffa fiber is incorporated. Luffa fillers enhance the porosity of Polyurethane foam, which is the dominating factor influencing the value of the sound absorption coefficient. Both rigid and flexible foams were developed with 5, 10 and 15 percentages of filler loaded. The samples are tested experimentally using the two-microphone impedance tube method and the measured result was compared with the numerical result, which is predicted from COMSOL Multiphysics. The experimental results of flexible foam demonstrate good agreement with numerical results. The results indicate that the addition of Luffa fibers enhances the sound absorption performance of flexible foam and deterioration in the rigid foam because of the high viscosity of castor oil polyol.