Computer Science
Editor's pick
Research Article
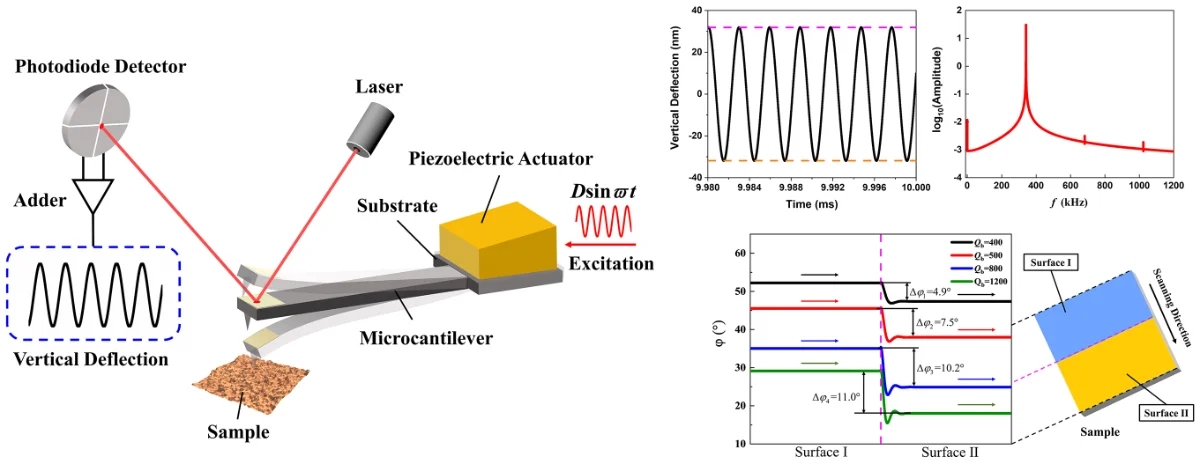
Simulation and experimental analysis of tip response of tapping mode atomic force microscope
By Anjie Peng, Yaxin Chen, Rui Guan, Zheng Wei
In this study, the vertical deflection responses of tapping mode atomic force microscope (TM-AFM) micro-cantilever tip are obtained by simulation and experiment. The results show that, under the blocking of the sample on one side, the steady-state response of the tip is still a sinusoidal form almost symmetrical about the equilibrium position. Furthermore, from the perspective of energy dissipation of the micro-cantilever system, the phases of two surfaces with different properties are simulated under different background dissipation. The result shows that eliminating partial background dissipation can increase the phase contrast between the two surfaces. These results are of significance for understanding the tip response and phase optimization in TM-AFM.
February 5, 2022
Computer Science
Most cited
Research Article
Research on 3D MFL testing of wire rope based on empirical wavelet transform and SRCNN
By Qihang Chen, Juwei Zhang, Bing Li
June 30, 2022
Computer Science
Most cited
Research Article
Analysis of unidirectional and bidirectional magnetic-thermal coupling of permanent magnet synchronous motor
By Fang Ding, Aiguo Wang, Qianbin Zhang
August 23, 2022
Computer Science
Most cited
Research Article
Discrete sliding mode control method for particle swarm optimization-based brushless DC motor of electric vehicle
By Fei Wang, Qiongzhen Mei, Xiaolei Xin
April 10, 2023
Computer Science
Most cited
Research Article
Dual direct torque control of doubly fed induction machine using second order sliding mode control
By Farid Boumaraf, Tarek Boutabba, Sebti Belkacem
February 20, 2021
Computer Science
Journal of Mechatronics and Artificial Intelligence in Engineering
Research Article
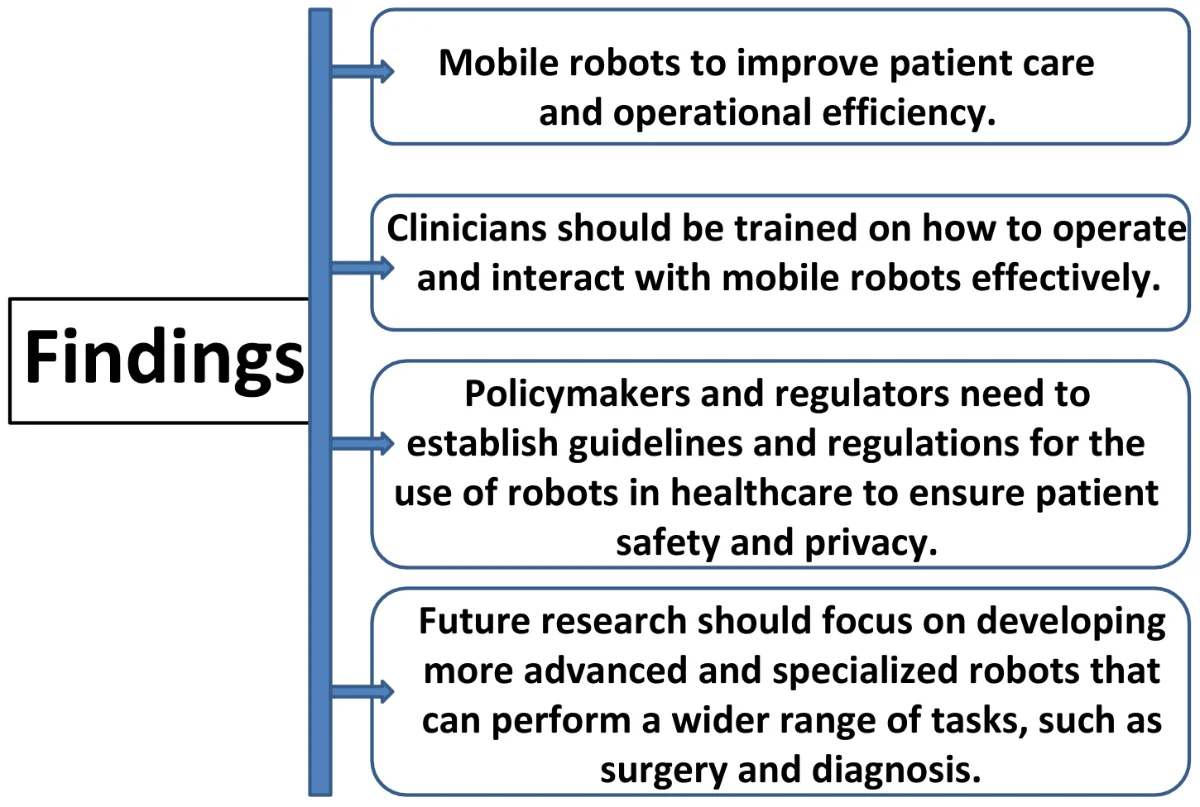
Challenges and opportunities for enhanced patient care with mobile robots in healthcare
Mobile robots are being used more frequently in healthcare environments to tackle a variety of issues, such as patient monitoring, drug administration, and support for healthcare professionals. However, considering how nascent the topic of deploying mobile robots in healthcare is, there hasn’t been much investigation into the potential benefits and drawbacks of doing so. The goal of this research study is to examine the current state of mobile robots in healthcare, the opportunities they present for enhancing patient care, and the difficulties that must be solved to take advantage of these advantages, including safety concerns, dependability and accuracy issues, and cost effectiveness issues. We identify critical elements that support the successful integration of mobile robots into healthcare environments, as well as potential drawbacks and ethical concerns such as patient privacy, informed consent, autonomy, and accountability related to their use, through a systematic review of the literature of mobile robot implementations in healthcare. Our results show the potential of mobile robots to enhance patient care by delivering more effective and efficient healthcare services, but they also emphasize the need for additional research and development to overcome the difficulties in integrating these robots into healthcare workflows. In the end, this research intends to provide a basis for future research and development in this fascinating and quickly developing sector, as well as to contribute to a better understanding of the opportunities and constraints connected with the use of mobile robots in healthcare.
August 1, 2023
Informatics
Research Article
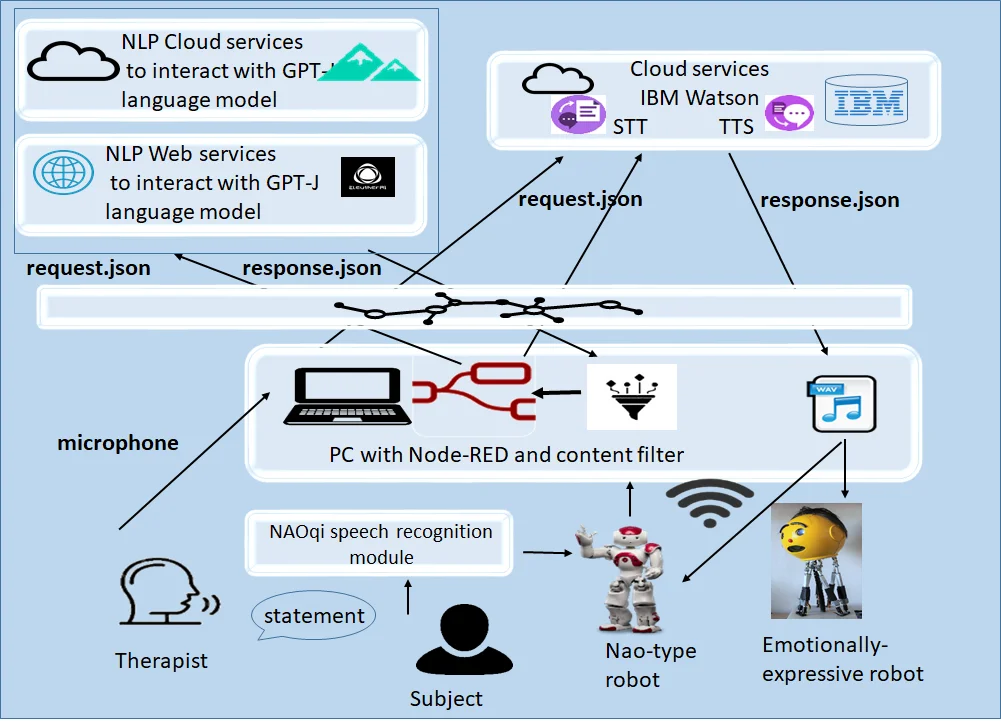
Making humanoid robots teaching assistants by using natural language processing (NLP) cloud-based services
Humanoid robots have a substantial potential to serve as teaching and social assistants. However, the expectations of the children from robots to interact like humans are huge. This study presents a general model for understanding the natural language in human-robot interaction by applying Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) language models as a service in the Internet of Things. Thus, the physical presence of the robot can help in fine-tuning the GPT model by prompts derived from the environmental context and subsequent robot actions for embodiment understanding of the GPT outputs. The model uses web or cloud services for Natural Language Processing (NLP) to produce and play human-like text, question answering or text generation. Verbal questions are processed either via a local speech recognition software or via a Speech-to-Text (STT) cloud service. The converted question into machine-readable code is sent to one of the GPT language models with zero- or few-shot learning prompts. GPT-J model has been tested and deployed either in the web or cloud with options for varying the parameters for controlling the haphazardness of the generated text. The robot produces human-like text by using Text-to-Speech (TTS) cloud services that convert the response into audio format rendered on the robot to be played. Useful requirements how the model to be used in order to be feasible were determined based on the evaluation of the outputs given from the different NLP and GPT-J web or cloud-services. We designed and implemented the model in order to be used by a humanoid NAO-type robot in the speech language therapy practice, however it can be used for other open-source and programmable robots and in different contexts.
June 30, 2022
Informatics
Research Article
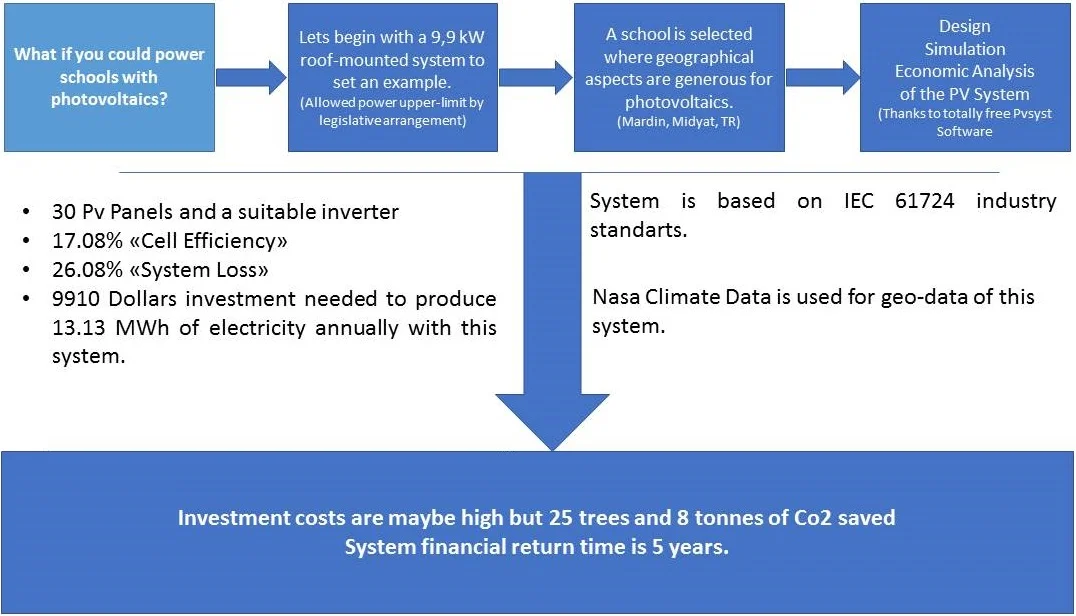
Powered by the sun: designing and analyzing technical and economic aspects of a school sustained by photovoltaics
Turkey has a young population. Accordingly, 66849 schools are serving under the Ministry of National Education. This amount of school naturally causes large amounts of electrical energy demand. Supporting even a small part of these schools with renewable energy sources will provide enormous economic and environmental contributions. Moreover, school buildings often share a template architecture, so a design can be reused, with some modifications over and over again. In this study, the PVsyst software is used to design a 9.9 kWp, roof-mounted, and grid-connected photovoltaic system. The technical and economic consequences of the study are widely reported within. IEC 61724 standards, which is a framework solar industry standard, is applied. Depending on the results, the system can generate 13.13 MWh of electricity annually, 6.43 MWh of which the consumer uses, and 6.70 MWh could be sold to the network. Selling electricity is limited by legislative regulations. But the demand for energy is a fact that never changes. As a result, PV cell efficiency is 17.09 %, and total system loss was approximately 26.18 %. The project cost was calculated as roughly $9912 in the year 2020, based on current prices for a standard system. Total economic earnings from sales are determined as approximately $1375. The return period of the investment was calculated as five years. It is anticipated that the engineering practice carried out in this study will prevent 8 tons of CO2 emissions annually and will save approximately 25 trees per year. It is recommended that this study be put into practice and disseminated.
June 30, 2020
Informatics
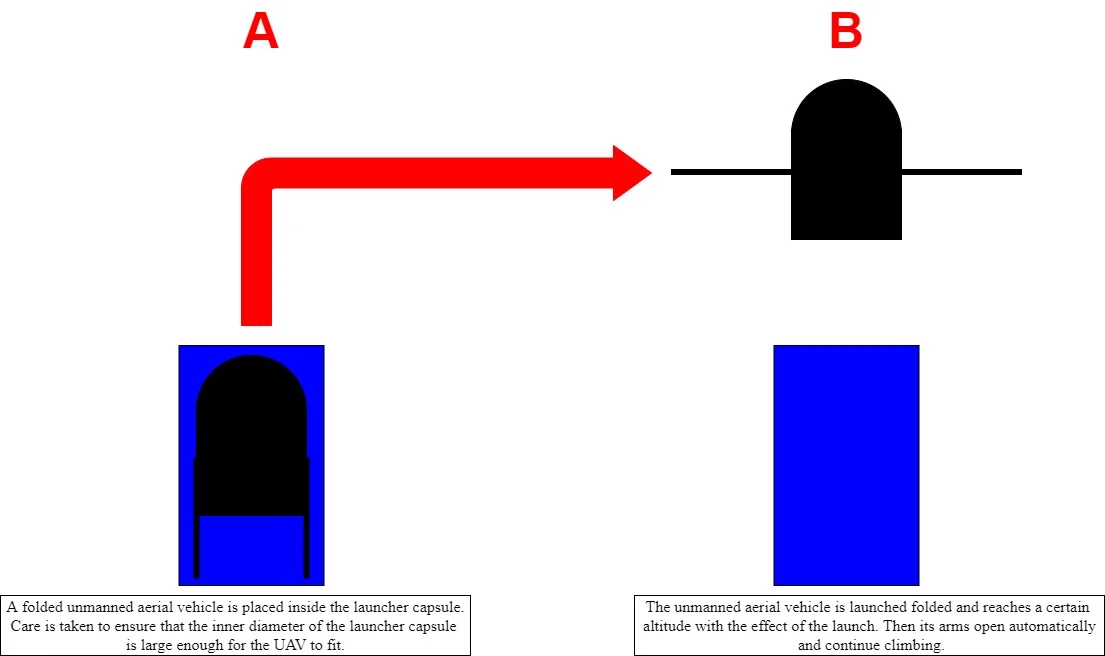
Research Article
Launchable rotary wing UAV designs and launch mechanism designs for rotary wing UAV
In recent years, rotary-wing unmanned aerial vehicles have been used in many areas. Rotary wing unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) can carry different payloads according to their duties. For example; if they carry cameras, they are used for reconnaissance / surveillance, cargo if they carry cargo, agriculture if they carry pesticides, mapping if they carry an advanced camera and mapping system, and communication if they carry a base station or relay. Rotary-wing unmanned aerial vehicles are usually commanded to take off manually by a trained UAV operator. Before takeoff, the rotary-wing unmanned aerial vehicle is prepared for take-off by the UAV operator and this preparation takes approximately five minutes. It takes time for rotary-wing unmanned aerial vehicles to take off from the runway and reach their cruising speed, causing time loss in critical areas. A rotary-wing unmanned aerial vehicle launch assembly and a rotary-wing unmanned aerial vehicle with an opening mechanism that can open the thrust arms after launch and continue to fly can be the solution to this time loss. Rotary-wing drones capable of launching and without the intervention of the UAV operator will play an important role in emergency response and defense, where situational awareness is often required. For example; firefighters responding to fires can take advantage of the ability to quickly launch rotary-wing unmanned aerial vehicles from a stationary or moving fire truck. Thanks to the day / thermal camera on the launched rotary wing unmanned aerial vehicles, valuable information can be obtained about the progress of the fire and the damage caused by the fire. Thanks to rapid awareness, the fire can be intervened and fought faster. Similarly, military personnel can quickly deploy launchable rotary-wing drones for reconnaissance and surveillance and perform their duties. In order to be applicable to various types of missions, it is important that the rotary wing unmanned aerial vehicle be portable and low in volume. Since the launchable rotary-wing unmanned aerial vehicle proposed in the thesis has an arm release mechanism after launch, it can automatically open and generate thrust after launching its arms. In this way, it helps lower volume coverage before being launched. This also reduces air friction during launch. It can be deployed to autonomous systems effortlessly as it has closed package, mobile and self-arm management. Different mechanisms will be studied to create an efficient design. A mechanism that allows it to open its arms in a short time will be used in the self-arm-opening management design. Throwable rotary wing unmanned aerial vehicle and launch mechanism will be designed and 3D printers will be used for prototype.
December 23, 2021
Informatics
Journal of Mechatronics and Artificial Intelligence in Engineering
<p>Recent advancements and practical applications focusing on the integration of mechatronics and artificial intelligence</p>
APC
Free of charge
You might also like
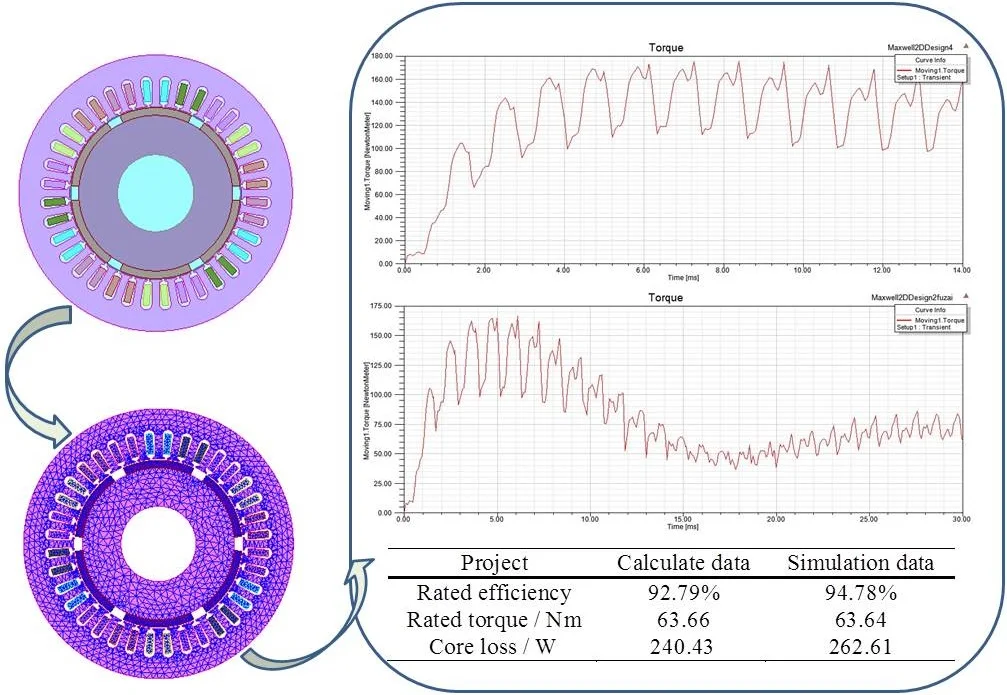
Most downloaded
Research Article
Design and analysis of driving motor system for hybrid electric vehicle
By Qiping Chen, Jiacheng Wei, Fanhong Zeng, Qiang Xiao, Hui Chen
In order to improve the reliability and stability of hybrid electric vehicle driving motor system, according to the performance parameters of the hybrid electric vehicle, the driving motor system is designed and analyzed for the hybrid electric vehicle. Based on the performance parameters of the hybrid electric vehicle, the power parameters of the permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) are calculated and determined, then the parameters of the stator core, the permanent magnet and the rotor core are designed and calculated, as well as other main characteristic parameters of the driving motor system are calculated. The model of a PMSM is established and simulated by ANSOFT Maxwell according to the obtained motor parameters, and then the steady state and transient state of the driving motor are simulated in different working points, and the electromagnetic and performance curves are combined to determine the overall performance requirements of the driving motor, which can be used to match the hybrid electric vehicle. The simulation results show that the designed PMSM can be used to match the hybrid electric vehicle and meet the performance requirements of the vehicle. The final simulation analysis results are in good agreement with the theoretical calculation results, which indicates that this method can be used to afford a theoretical basis to reduce the cogging torque and optimize the in-wheel motor of electric vehicle in the future.
March 31, 2020
Computer Science
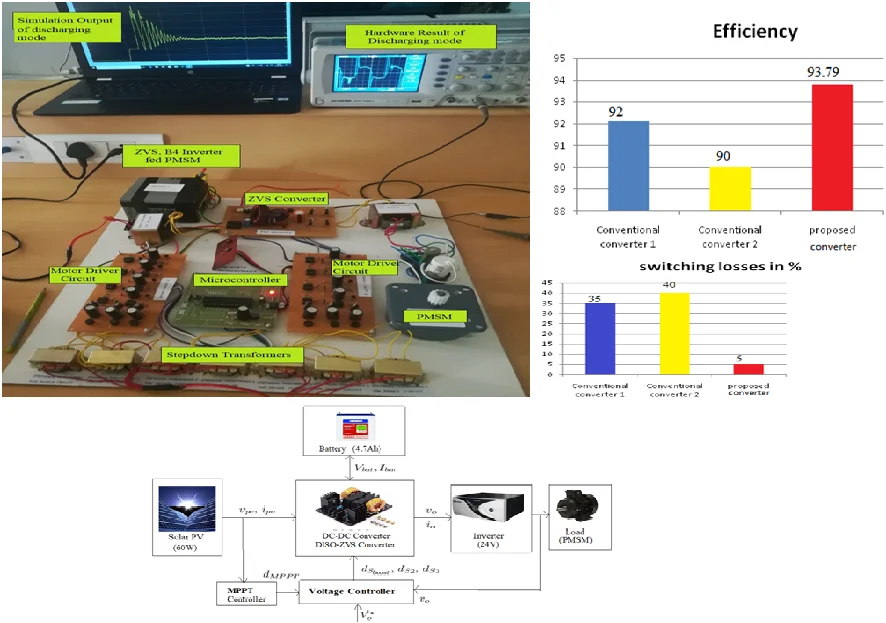
Most downloaded
Research Article
Implementation of standalone dynamic solar array fed permanent magnet synchronous motor drive using zero voltage switching resonant converter for the reduction of switching losses and oscillations
By Chelliah Muniyandi, Suresh Kumar Rajagopal
The Proposed research deals implementation of standalone dynamic solar array fed permanent magnet synchronous motor drive using zero voltage resonant switch converter for the reduction of switching losses and oscillations. The closed loop control voltage strategy has been proposed for power flow management between solar photovoltaic (PV), battery, motor load and to maintain constant load voltage to perform continuous MPPT operation of solar PV. For improving the efficiency and to reduce vibration across the load SPV array fed Zero Voltage Switching (DISOZVS) Resonant Converter with permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) drive is proposed. The DISOZVS resonant converter with suitable switching operation accomplishes for the purpose of reducing the Switching losses. The ZVS converter is constructed by a buck-boost circuit, which is operated as a buck circuit when charging and a boost circuit when discharging. So, we can use many power related systems, which improves efficiency, lower losses and higher performance. The various dynamics and oscillations of standalone SPV array is analysed in the proposed research. The performance of the proposed system is simulated in MATLAB/Simulink atmosphere and various parameters outputs are carried. A hardware prototype of the proposed system has been fabricated for the proposed converter and various analysis were incorporated. The working of the proposed scheme for the different levels of input solar insolation and Load power demand has been satisfactorily demonstrated for both simulation and experimental compared to conventional it results more efficient with reduced losses and oscillations.
August 15, 2019
Computer Science
Simulation of three-phase short circuit electromagnetic transient process of synchronous generator
This paper studies the transient process of synchronous generator after three-phase short circuit, deduces the expression of stator current in the transient process of synchronous generator, and verifies the theoretical conclusion through simulation. After the short circuit occurs, the electromagnetic transient process is complex. In the electromagnetic transient process, the stator current and rotor current of synchronous generator appear attenuation oscillation due to direct-axis reactance, cross-axis reactance, transient reactance and sub-transient reactance. Based on the basic principle of synchronous generator, this paper analyzes the analytical expressions of stator straight axis current, stator cross axis current and total current. After that, the simulation model is built in Matlab/Simulink, and the simulation results are consistent with the theoretical analysis results. This simulation method provides convenience for analyzing the transient process of synchronous generator and has good engineering application value.
A novel hybrid topology for power quality improvement using multilevel inverter for the reduction of vibration and noise in brushless DC motor for industrial applications
The proposed research involves the design and implementation of a novel hybrid Topology for Power Quality Improvement using Multilevel Inverter to reduce vibration and noise in BLDC motor for industrial applications. The utility of power electronics device plays a vital role for various applications in recent days. Similarly, the power consumption is also important for all processing units. The power electronic devices contain a lot of converters for processing the energy. During such cases, the harmonics are produced in different ways. Hence, a system analysis is necessary to find the problem at conventional methods. Hence the problem is identified on the distribution static compensator (DSTATCOM) component module whose harmonics are high, and it is important module for the circuit, hence preventive action to be taken to reduce the harmonics. To limit or reduce the harmonics, it is required to modify the triggering mechanism and control unit of Multi level inverter. Hence, the proposed hybrid method is implemented with the developed H-bridge and diode clamped topology with a brushless dc motor. In addition, the vibrations and the noise level are also reduced due to the reduced total harmonic distortion. The proposed module is simulated on MATLAB Simulink, and an experimental analysis is carried out to verify functionality tools with various operating conditions, the proposed method proves more efficient than the switches and complex networks present in traditional methods.